Unveiling The Secrets Of The Atmosphere: Understanding Air Pressure Maps
Unveiling the Secrets of the Atmosphere: Understanding Air Pressure Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the Atmosphere: Understanding Air Pressure Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of the Atmosphere: Understanding Air Pressure Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of the Atmosphere: Understanding Air Pressure Maps
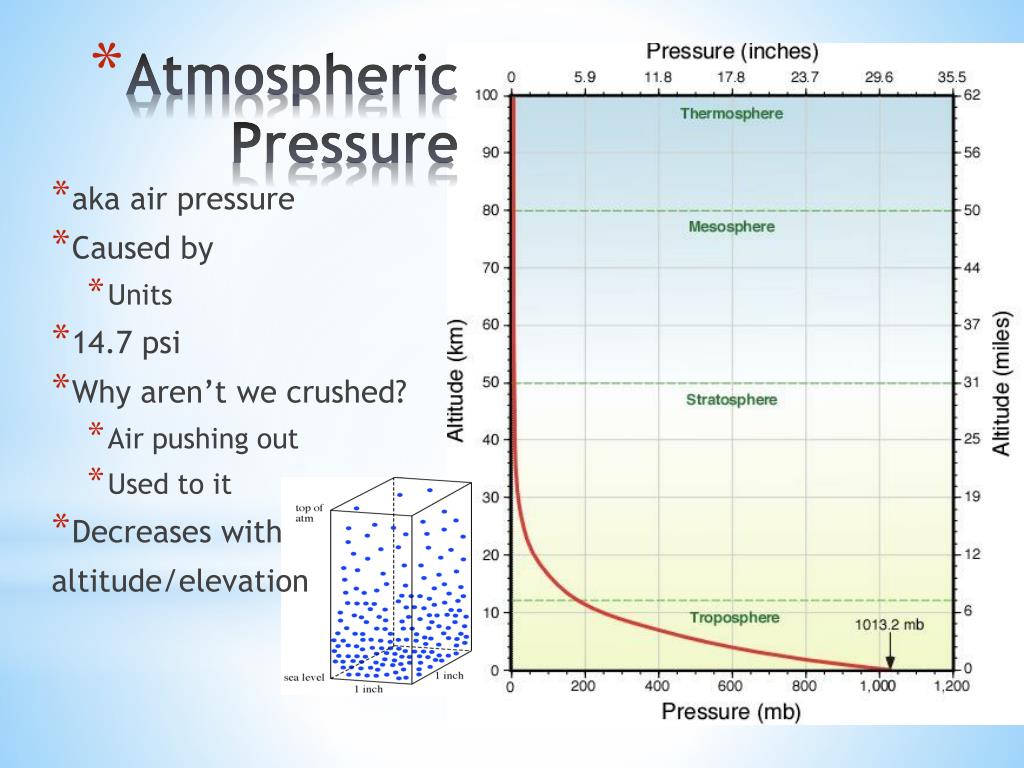
The Earth’s atmosphere is a dynamic and complex system, constantly in motion and subject to a myriad of forces. Air pressure, the force exerted by the weight of the atmosphere, is a fundamental element that governs weather patterns and influences our daily lives. Air pressure maps, visual representations of atmospheric pressure across a region, serve as powerful tools for understanding and predicting weather phenomena. By deciphering the patterns and variations depicted on these maps, meteorologists gain valuable insights into the forces that shape our weather, enabling them to issue accurate forecasts and warnings.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Air Pressure
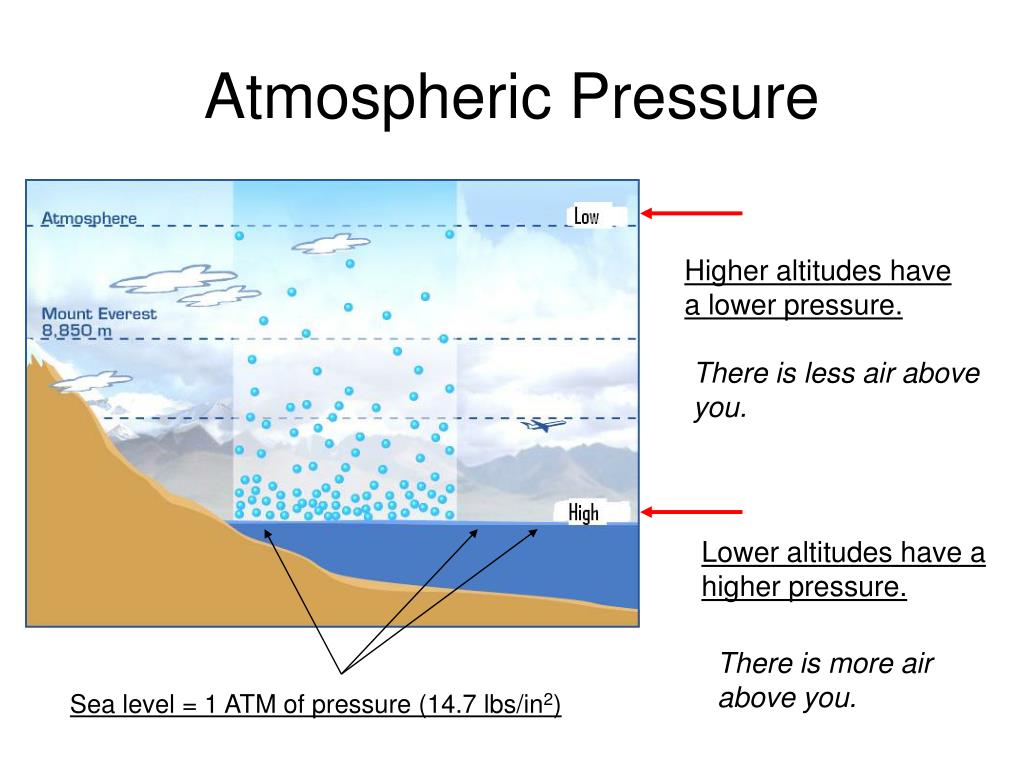
Air pressure is measured in units of millibars (mb) or hectopascals (hPa). High pressure systems are characterized by descending air, creating a sense of stability and generally clear skies. Conversely, low pressure systems are associated with rising air, leading to cloud formation, precipitation, and often stormy conditions. Air pressure maps visually represent these variations, providing a snapshot of the atmospheric conditions at a given time.
Decoding the Symbols and Patterns
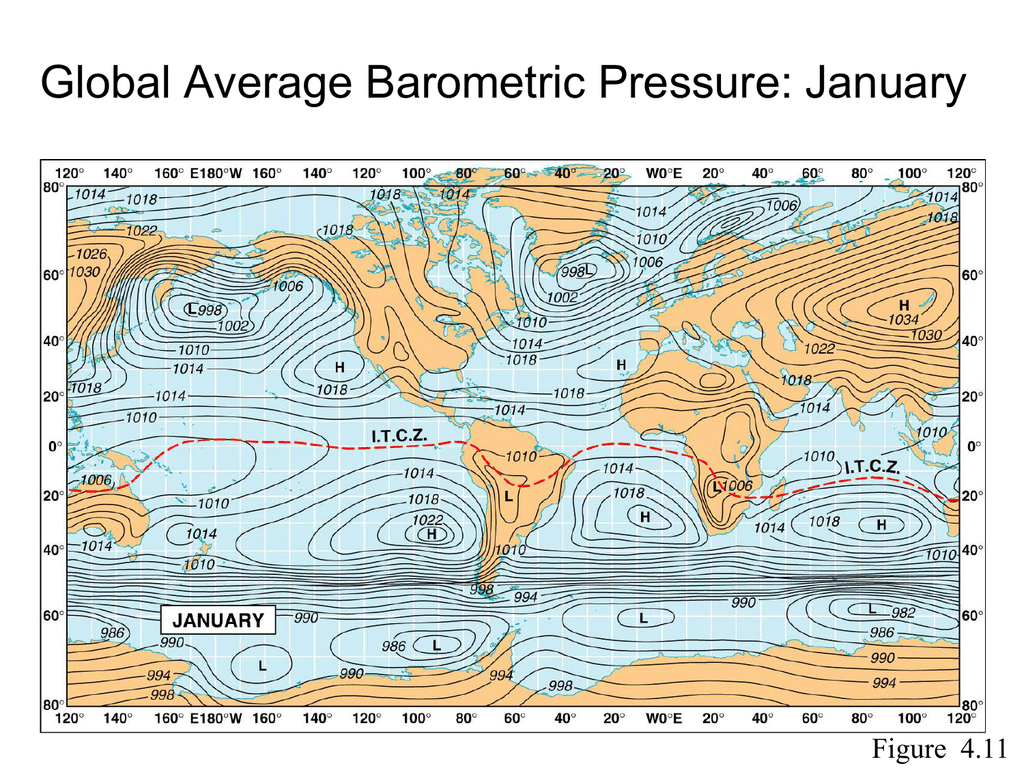
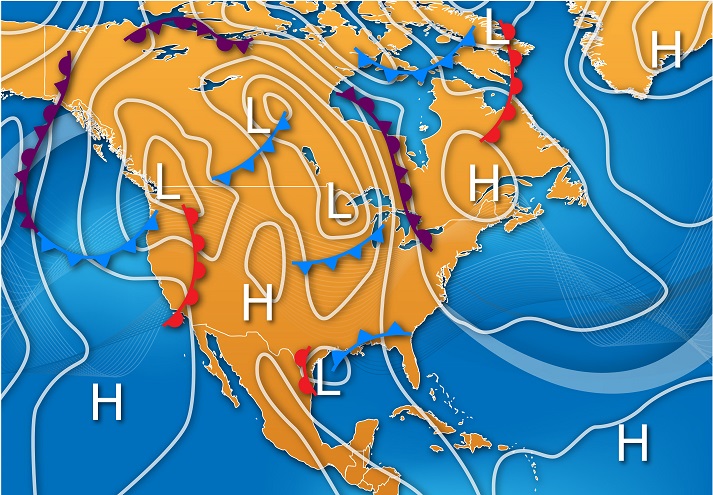
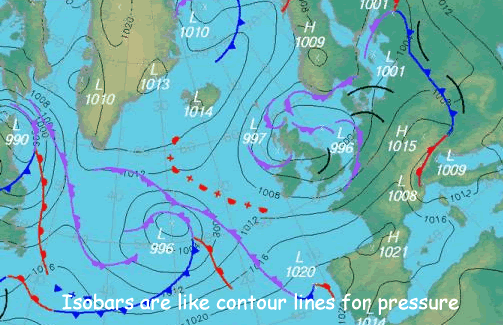
Air pressure maps employ a standardized system of symbols and colors to convey information about atmospheric pressure. Isobars, lines connecting points of equal pressure, are the most prominent feature on these maps. Closely spaced isobars indicate a steep pressure gradient, suggesting strong winds and potentially turbulent weather. Conversely, widely spaced isobars indicate a gentle pressure gradient, often associated with calm and stable conditions.
The Importance of Air Pressure Maps in Weather Forecasting
Air pressure maps are indispensable tools for weather forecasting, providing meteorologists with crucial information for predicting weather patterns. By analyzing the pressure gradients, wind patterns, and the movement of high and low pressure systems, meteorologists can anticipate the development of storms, predict precipitation, and estimate wind speeds. This information is crucial for issuing timely warnings and advisories, enabling communities to prepare for potentially hazardous weather events.
Beyond Weather Forecasting: Applications of Air Pressure Maps
The applications of air pressure maps extend beyond weather forecasting, influencing various aspects of our lives. For example:
- Aviation: Pilots rely on air pressure maps to navigate safely, understanding wind patterns and atmospheric conditions that can affect flight paths and altitudes.
- Marine Navigation: Sailors utilize air pressure maps to plan voyages, predicting wind direction and strength, which is essential for safe navigation and efficient sailing.
- Environmental Monitoring: Air pressure maps are used to monitor the movement of pollutants and hazardous substances in the atmosphere, aiding in environmental protection and disaster preparedness.
- Climate Studies: Long-term records of air pressure data provide valuable insights into climate change, revealing trends and patterns that influence global weather systems.
FAQs about Air Pressure Maps
1. How are air pressure maps created?
Air pressure maps are generated by collecting data from a network of weather stations and satellites. These stations measure atmospheric pressure at ground level and aloft, while satellites provide data on pressure variations across vast areas. This data is then processed and displayed on maps using a variety of visualization techniques.
2. What are the different types of air pressure maps?
There are several types of air pressure maps, each tailored to specific purposes. Synoptic maps provide a broad overview of atmospheric pressure across a region, while surface maps focus on pressure at ground level. Upper-air maps depict pressure at different altitudes, revealing the structure and movement of atmospheric systems.
3. How can I interpret an air pressure map?
Interpreting an air pressure map requires understanding the symbols and patterns used. Identify the isobars, which indicate areas of equal pressure. Observe the spacing between isobars to determine the pressure gradient. Look for high and low pressure systems, noting their movement and potential for influencing weather patterns.
4. What are the limitations of air pressure maps?
Air pressure maps provide a snapshot of atmospheric conditions at a specific time. Weather patterns are dynamic, and changes can occur rapidly. Therefore, air pressure maps are not a perfect predictor of future weather, and forecasts should be interpreted with caution.
5. How can I access air pressure maps?
Air pressure maps are readily available from various sources, including:
- National Weather Services: Most countries have national weather services that provide access to real-time air pressure maps.
- Weather Websites and Apps: Numerous websites and mobile applications offer interactive air pressure maps, often with additional weather information and forecasting tools.
- Scientific Data Repositories: Scientific organizations and research institutions often make air pressure data and maps available for public access.
Tips for Understanding Air Pressure Maps
- Start with the basics: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and patterns used on air pressure maps.
- Focus on the isobars: Pay close attention to the spacing between isobars to understand the pressure gradient.
- Identify high and low pressure systems: Locate the areas of high and low pressure and note their movement.
- Consider the surrounding weather: Relate the air pressure patterns to other weather factors, such as temperature, wind, and precipitation.
- Consult multiple sources: Compare data from different sources to obtain a comprehensive understanding of atmospheric conditions.
Conclusion
Air pressure maps are essential tools for understanding and predicting weather patterns, influencing various aspects of our lives from aviation and marine navigation to environmental monitoring and climate studies. By deciphering the symbols, patterns, and variations depicted on these maps, we gain invaluable insights into the forces that shape our weather, enabling us to navigate the complexities of the atmosphere and make informed decisions about our safety and well-being. As technology continues to advance, air pressure maps will continue to evolve, providing even greater accuracy and precision in forecasting and understanding the dynamics of our planet’s atmosphere.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of the Atmosphere: Understanding Air Pressure Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Future: A Deep Dive Into SAP’s Roadmap
- Vanguard: A Comprehensive Exploration Of The Map
- Navigating The African Continent: Understanding Longitude And Latitude
- Unpacking The Geography Of East Europe And Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
- Interstate 5: A Vital Artery Connecting The West Coast
- Navigating Paradise: A Comprehensive Guide To Sandals Resort Locations
- A Coastal Tapestry: Exploring Washington State’s Diverse Shoreline
- Navigating The Beauty Of Utah: A Comprehensive Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply