Unveiling The Power Of Tree Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Unveiling the Power of Tree Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Tree Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Tree Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Tree Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Power of Tree Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of Tree Maps
- 3.2 Delving Deeper into the Advantages of Tree Maps
- 3.3 Applications of Tree Maps Across Diverse Fields
- 3.4 Unveiling the Mechanics of Tree Map Creation
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions About Tree Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Tree Map Implementation
- 3.7 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Visual Representation
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Power of Tree Maps: A Comprehensive Guide

In the realm of data visualization, the ability to effectively represent complex information is paramount. While bar charts, pie charts, and scatter plots serve their purposes, they often struggle to convey intricate hierarchical relationships within data sets. Enter the tree map, a powerful visualization tool that excels in illustrating hierarchical structures and proportional relationships, offering a clear and insightful view of complex data.
Understanding the Essence of Tree Maps
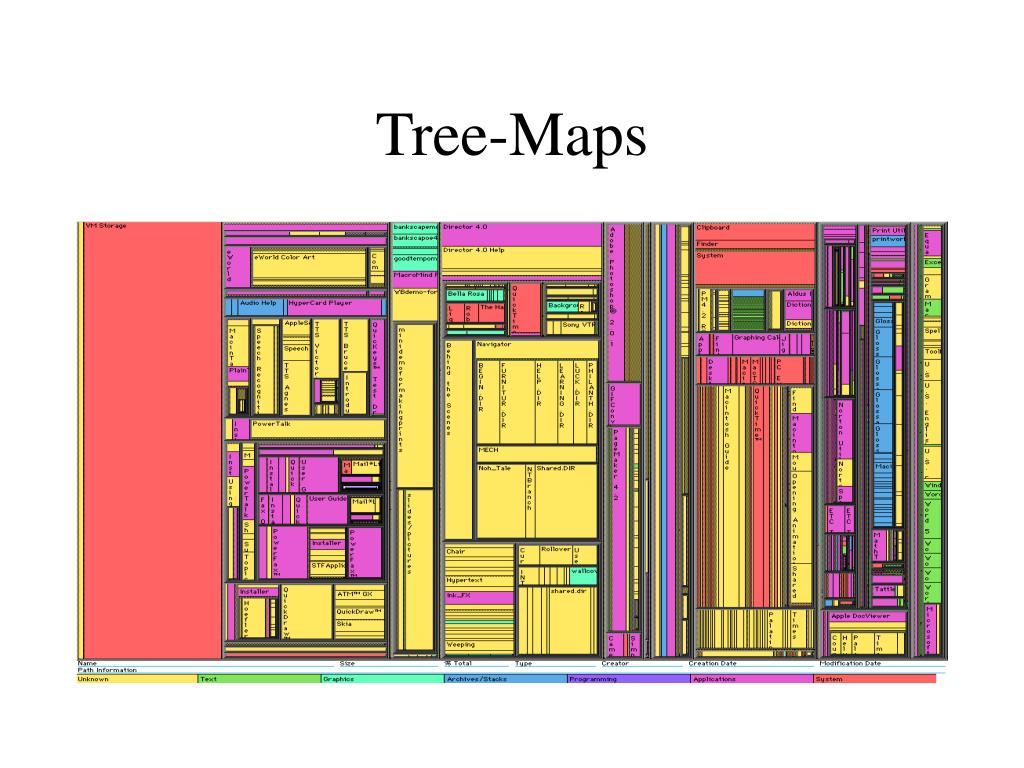
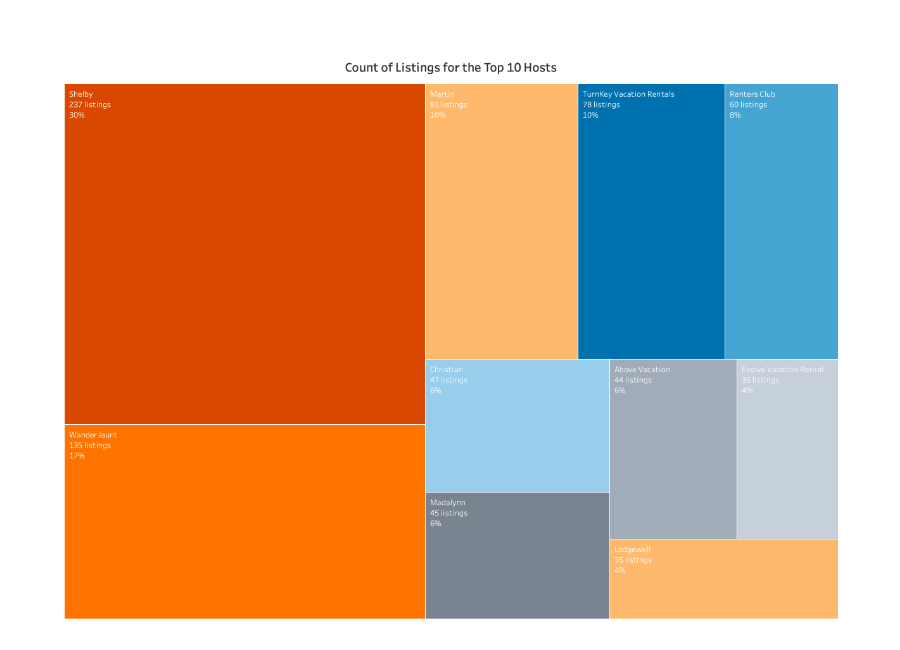
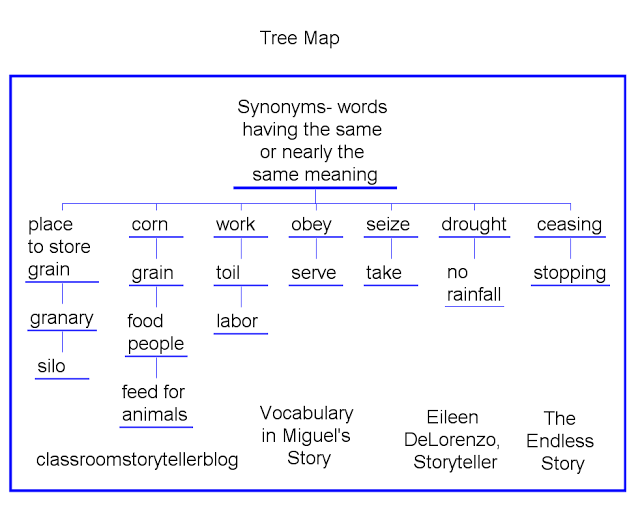
A tree map, as the name suggests, resembles a hierarchical tree structure. It divides a rectangular area into smaller rectangles, each representing a specific data category or sub-category. The size of each rectangle corresponds to its value, while its color often reflects an additional attribute or dimension. This visual representation allows for a simultaneous understanding of both the hierarchical structure and the relative proportions of data within each level.
Delving Deeper into the Advantages of Tree Maps
The utility of tree maps lies in their ability to:
- Reveal Proportional Relationships: The varying sizes of rectangles intuitively demonstrate the relative significance of different data elements, providing a clear understanding of their contribution to the whole.
- Illustrate Hierarchical Structures: The nested arrangement of rectangles mirrors the hierarchical organization of the data, facilitating the comprehension of complex relationships between different categories.
- Enhance Data Exploration: Tree maps encourage interactive exploration, allowing users to drill down into specific categories by clicking on individual rectangles, revealing further details and sub-categories.
- Promote Data Comparison: By representing multiple data points within a single visualization, tree maps facilitate easy comparison of values across different categories and levels of hierarchy.
- Reduce Cognitive Load: Compared to traditional charts, tree maps offer a more efficient way to process and understand large amounts of data, minimizing cognitive overload.
Applications of Tree Maps Across Diverse Fields
Tree maps find widespread applications in various fields, including:
- Business Analytics: Analyzing sales data by product category, identifying the most profitable segments, and understanding market trends.
- Finance: Visualizing portfolio allocations, tracking investment performance, and identifying areas of risk.
- Marketing: Examining website traffic patterns, identifying popular content, and understanding user behavior.
- Healthcare: Analyzing patient demographics, tracking disease prevalence, and identifying areas of resource allocation.
- IT Management: Monitoring server performance, identifying resource bottlenecks, and understanding network traffic patterns.
Unveiling the Mechanics of Tree Map Creation
While the concept of tree maps is relatively straightforward, their creation involves specific techniques and considerations:
- Data Preparation: The data must be structured hierarchically, with clear parent-child relationships between categories. This may involve pre-processing and aggregation of raw data.
- Layout Algorithm: The arrangement of rectangles within the tree map is determined by a specific layout algorithm. Common algorithms include Squarified, Strip, and Treemap. Each algorithm optimizes for different visual properties, influencing the layout and readability of the map.
- Color Scheme: The choice of color scheme plays a crucial role in conveying information and enhancing visual clarity. Color can be used to highlight specific categories, represent different values, or guide the user’s attention.
- Interactive Features: Many tree map tools offer interactive features such as drill-down capabilities, filtering, and zooming, allowing users to explore the data in detail.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions About Tree Maps
1. What are the limitations of tree maps?
While powerful, tree maps have limitations. They may struggle to represent complex relationships beyond a single hierarchy, and the visual representation of smaller values can be challenging. Additionally, the effectiveness of tree maps can be influenced by the chosen layout algorithm and color scheme.
2. What are the best tools for creating tree maps?
Several software tools offer tree map functionality, including Tableau, Power BI, Excel, and Google Sheets. Specialized tools like TreeMapJS and D3.js provide greater flexibility and customization.
3. How can I choose the right layout algorithm for my tree map?
The choice of layout algorithm depends on the specific data and visualization goals. Squarified algorithms prioritize rectangular shapes, while Strip algorithms focus on maximizing the use of space.
4. What are some best practices for designing effective tree maps?
- Use clear and concise labels for each rectangle.
- Choose a color scheme that enhances readability and highlights relevant information.
- Consider the overall visual impact and ensure the map is easily digestible.
- Provide interactive features to allow users to explore the data in detail.
Tips for Effective Tree Map Implementation
- Start with a Clear Objective: Define the specific insights you want to convey through the tree map.
- Choose the Right Data: Ensure the data is structured hierarchically and appropriate for tree map visualization.
- Experiment with Layout Algorithms: Try different layout algorithms to find the one that best suits your data and visual goals.
- Optimize Color Scheme: Select colors that enhance readability and highlight relevant information.
- Prioritize User Experience: Design the tree map for optimal user interaction and ease of understanding.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Visual Representation
Tree maps offer a compelling and efficient method for visualizing complex hierarchical data. By leveraging their ability to reveal proportional relationships, illustrate hierarchical structures, and enhance data exploration, they empower users to gain deeper insights from their data. As data complexity continues to increase, tree maps will undoubtedly play an increasingly significant role in helping organizations navigate the vast landscape of information and make informed decisions.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Tree Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Future: A Deep Dive Into SAP’s Roadmap
- Vanguard: A Comprehensive Exploration Of The Map
- Navigating The African Continent: Understanding Longitude And Latitude
- Unpacking The Geography Of East Europe And Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
- Interstate 5: A Vital Artery Connecting The West Coast
- Navigating Paradise: A Comprehensive Guide To Sandals Resort Locations
- A Coastal Tapestry: Exploring Washington State’s Diverse Shoreline
- Navigating The Beauty Of Utah: A Comprehensive Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply