Unraveling The Body’s Internal Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide To Muscle Anatomy
Unraveling the Body’s Internal Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to Muscle Anatomy
Related Articles: Unraveling the Body’s Internal Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to Muscle Anatomy
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Body’s Internal Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to Muscle Anatomy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Body’s Internal Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to Muscle Anatomy
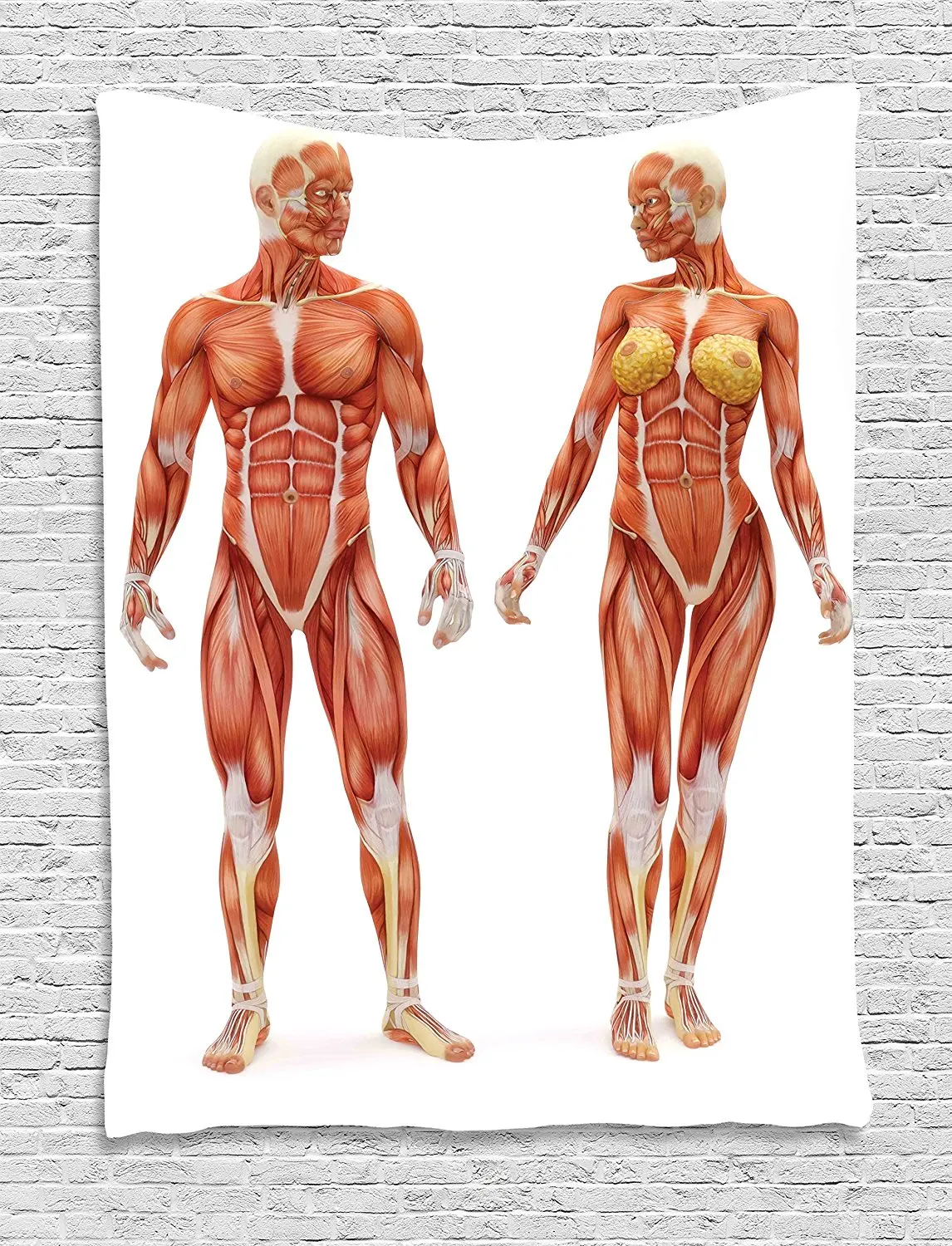
The human body is a marvel of intricate engineering, a symphony of coordinated movements orchestrated by a complex network of muscles. Understanding this intricate network, its individual components, and their interconnected functions is paramount for anyone seeking to optimize their physical performance, rehabilitate from injury, or simply gain a deeper appreciation for the body’s capabilities. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of muscle anatomy, exploring the concept of a muscle map, its significance, and its practical applications.
Understanding the Muscle Map: A Visual Representation of the Body’s Internal Landscape
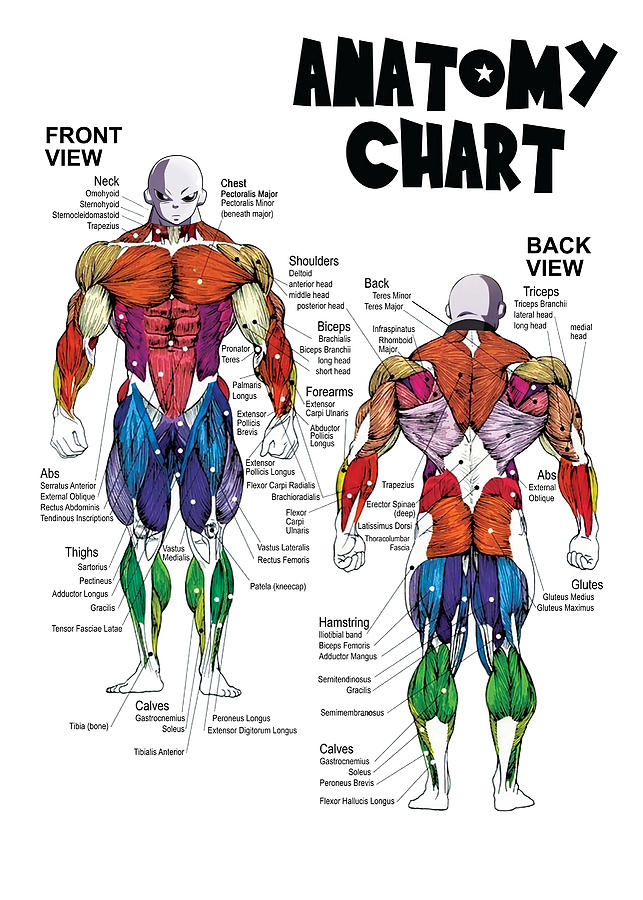
A muscle map is a visual representation of the skeletal muscles, their locations, and their primary functions. It serves as a roadmap, guiding individuals through the complex network of muscles that underpin movement, posture, and overall bodily function. These maps can vary in complexity, ranging from basic outlines highlighting major muscle groups to detailed anatomical illustrations showcasing individual muscle fibers and their intricate attachments.
The Significance of Muscle Maps: A Gateway to Understanding and Optimizing Body Function
The benefits of understanding muscle anatomy through muscle maps extend beyond academic curiosity, offering practical applications for various disciplines:
-
Fitness and Exercise: Muscle maps empower individuals to target specific muscle groups effectively during exercise, ensuring optimal training routines for desired outcomes. Recognizing the location and function of muscles allows for tailored exercises that promote strength, endurance, flexibility, and overall physical fitness.
-
Rehabilitation and Injury Prevention: Understanding muscle anatomy is crucial for therapists and trainers involved in rehabilitation. Muscle maps aid in identifying the affected muscles, their roles in specific movements, and the appropriate exercises for restoring function and preventing future injuries.
-
Sports Performance: Elite athletes leverage muscle maps to analyze their movements, identify muscle imbalances, and develop targeted training programs that enhance performance and minimize risk of injury. Understanding the intricate interplay of muscles during complex movements is key to optimizing athletic prowess.
-
Pain Management: Muscle maps assist healthcare professionals in pinpointing the source of pain, guiding them in developing personalized treatment plans. By identifying the affected muscle or muscle group, practitioners can address the underlying cause of pain, leading to more effective interventions.
-
Improved Body Awareness: A deeper understanding of muscle anatomy fosters a greater appreciation for the body’s capabilities and limitations. This heightened awareness allows for better posture, more efficient movement, and a conscious approach to physical activity.
Navigating the Muscle Map: A Detailed Exploration of Major Muscle Groups
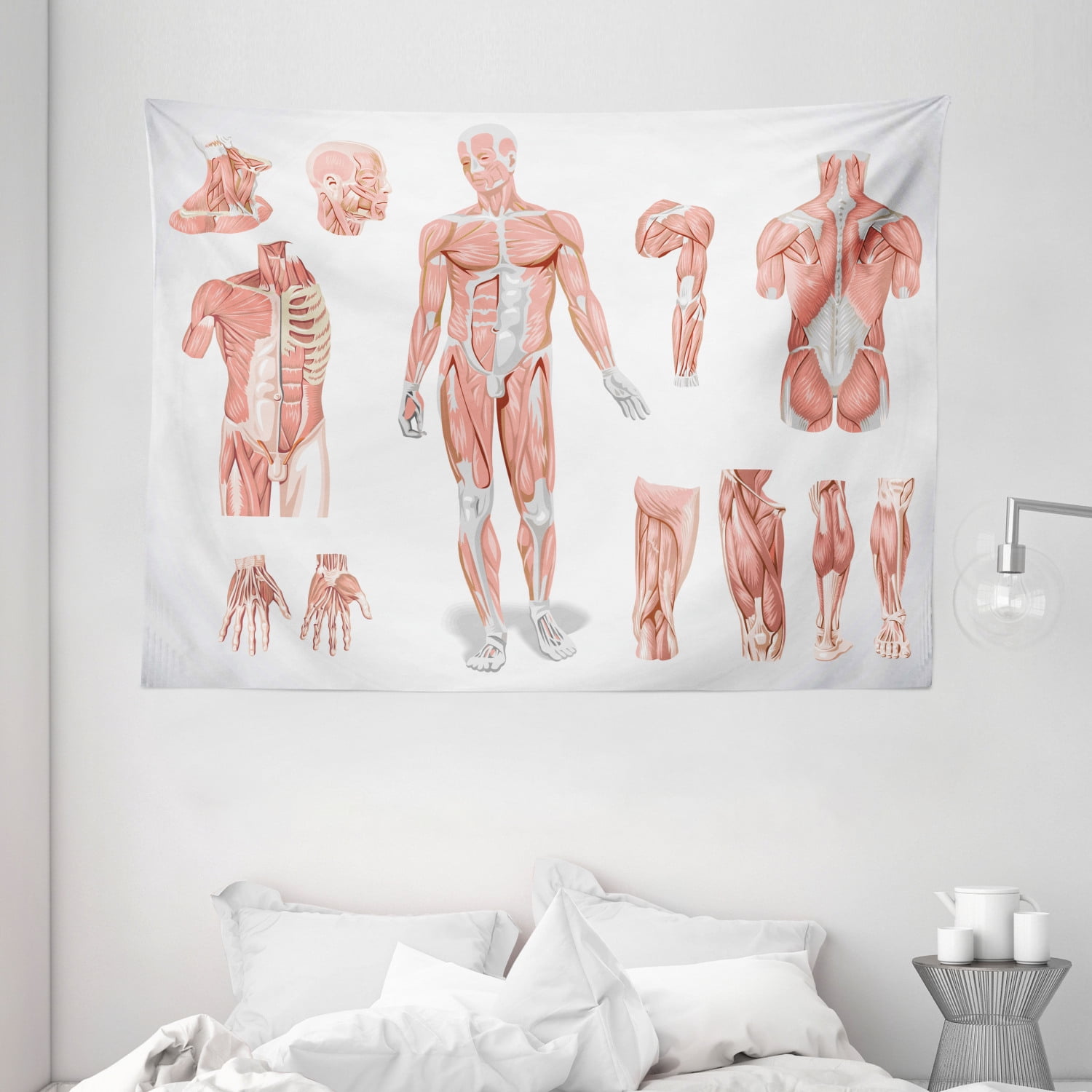
The human body boasts over 600 skeletal muscles, each playing a unique role in movement and overall function. For practical purposes, these muscles can be broadly categorized into major groups:
-
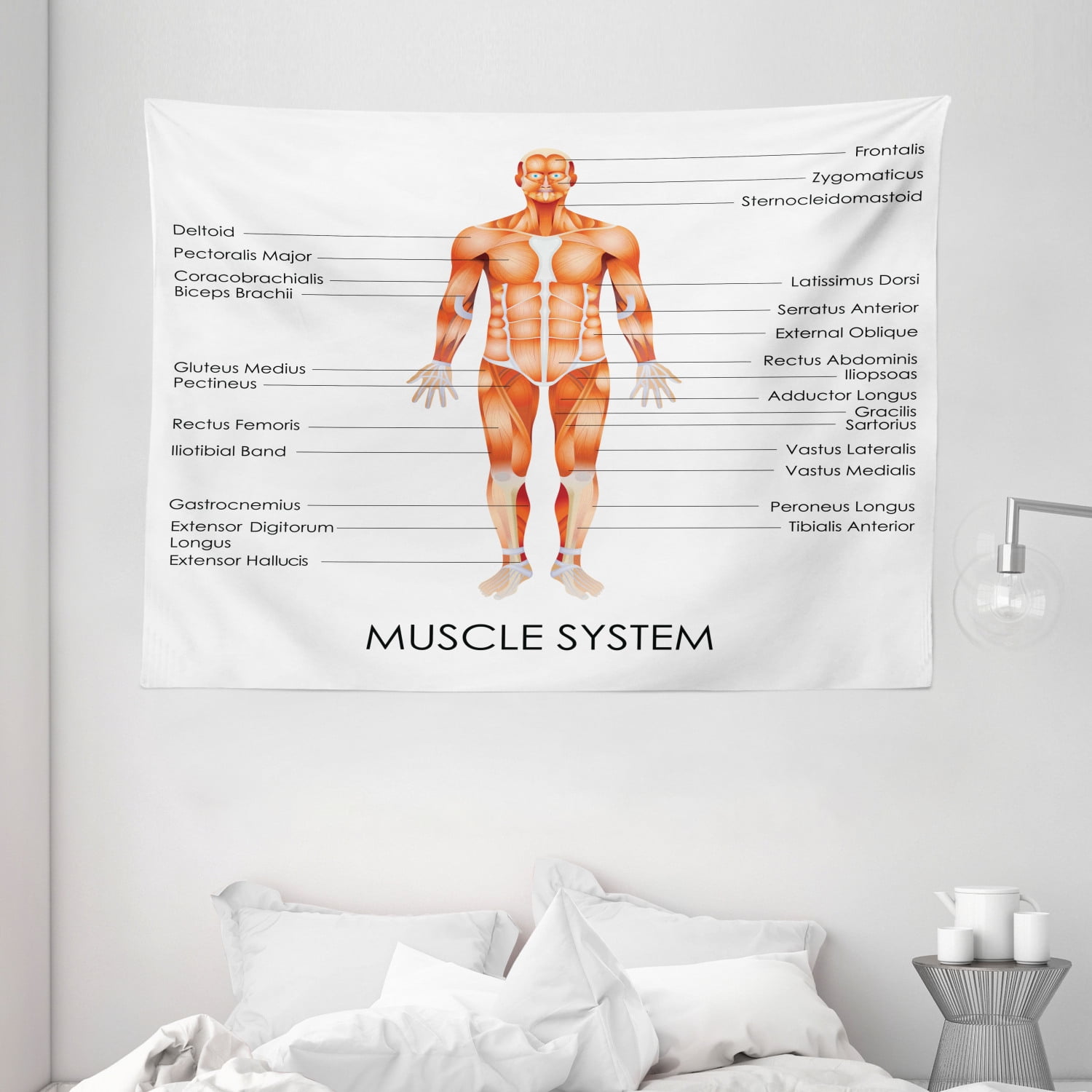
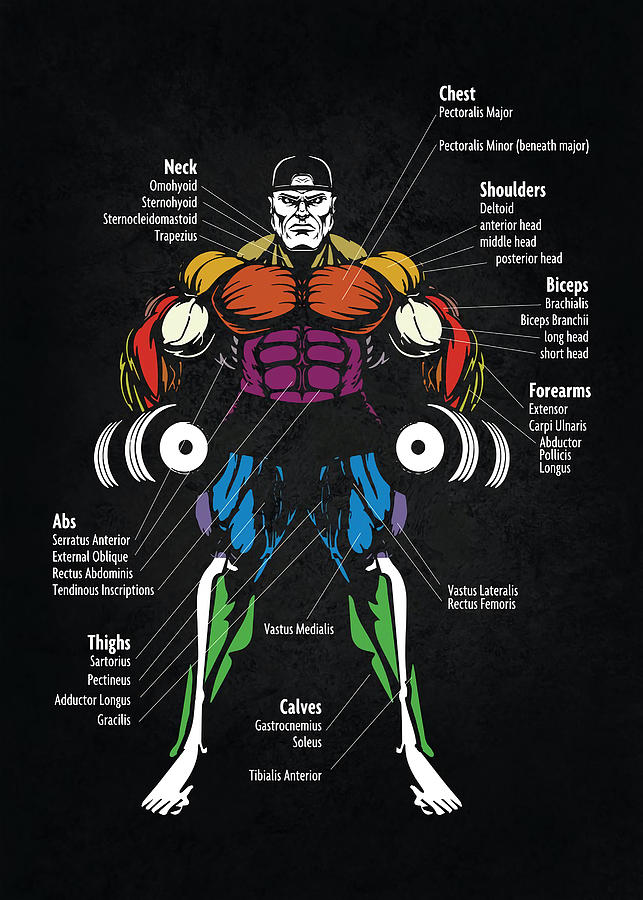
Head and Neck: This region houses muscles responsible for facial expressions, chewing, swallowing, and head movements. Notable muscles include the masseter (chewing), temporalis (chewing), sternocleidomastoid (neck flexion and rotation), and trapezius (shoulder elevation and retraction).
-
Shoulder and Upper Back: Muscles in this region facilitate shoulder movement, arm rotation, and posture. Key players include the deltoid (shoulder abduction), pectoralis major (chest and shoulder flexion), latissimus dorsi (back extension and arm adduction), and rotator cuff muscles (shoulder stability).
-
Arms and Forearms: This area encompasses muscles responsible for elbow flexion and extension, wrist movement, and hand manipulation. Significant muscles include the biceps brachii (elbow flexion), triceps brachii (elbow extension), brachioradialis (forearm flexion), and flexor/extensor carpi muscles (wrist movement).
-
Torso and Abdomen: Muscles in this region contribute to core stability, spinal movement, and breathing. Important muscles include the rectus abdominis (abdominal flexion), obliques (trunk rotation and lateral flexion), erector spinae (back extension), and diaphragm (breathing).
-
Legs and Feet: This region houses muscles that enable walking, running, jumping, and balance. Key muscles include the quadriceps femoris (knee extension), hamstrings (knee flexion), gluteus maximus (hip extension), gastrocnemius (ankle plantarflexion), and tibialis anterior (ankle dorsiflexion).
Exploring Muscle Actions: Understanding the Dynamics of Movement
Muscles function by contracting, generating force that pulls on bones, resulting in movement. The specific action of a muscle is determined by its location, attachment points, and the direction of its fibers. Understanding muscle actions is crucial for designing effective exercise programs and comprehending the mechanics of movement.
-
Agonist: The primary mover responsible for a specific action. For example, the biceps brachii is the agonist for elbow flexion.
-
Antagonist: The muscle that opposes the action of the agonist, providing control and stability. The triceps brachii acts as the antagonist to the biceps brachii during elbow flexion.
-
Synergist: A muscle that assists the agonist in performing an action. The brachialis muscle assists the biceps brachii in elbow flexion.
-
Fixator: A muscle that stabilizes a joint, preventing unwanted movement. The rotator cuff muscles act as fixators for the shoulder joint.
Muscle Maps: A Practical Tool for Personal and Professional Applications
Muscle maps are invaluable tools for individuals seeking to improve their physical well-being, optimize performance, or understand the intricate workings of their bodies. They provide a visual framework for comprehending muscle anatomy, enabling targeted training, effective rehabilitation, and enhanced body awareness.
FAQs: Addressing Common Inquiries About Muscle Maps
1. What is the best way to learn about muscle anatomy?
There are various methods for learning about muscle anatomy, including:
- Textbooks and Online Resources: Consult anatomical textbooks and online resources like anatomy atlases and interactive muscle maps.
- Anatomy Courses: Enroll in anatomy courses offered at universities, community colleges, or online platforms.
- Anatomical Charts and Models: Utilize anatomical charts and models to visualize muscle locations and relationships.
- Practical Application: Engage in exercises and physical activities that involve targeted muscle groups, enhancing your understanding through direct experience.
2. Are muscle maps useful for beginners in fitness?
Absolutely. Muscle maps provide a visual foundation for understanding the body’s structure, allowing beginners to target specific muscle groups effectively during exercise. They can help avoid common mistakes, ensure proper form, and maximize training results.
3. Can muscle maps help with pain management?
Understanding muscle anatomy can be beneficial for pain management. By identifying the affected muscle or muscle group, healthcare professionals can pinpoint the source of pain, leading to more effective treatment strategies.
4. What are some resources for finding detailed muscle maps?
Numerous resources offer detailed muscle maps, including:
- Anatomical Textbooks: Textbooks dedicated to anatomy and kinesiology often include comprehensive muscle maps.
- Online Anatomy Atlases: Websites like Visible Body and AnatomyTV provide interactive 3D muscle maps.
- Medical Illustration Websites: Websites like Medical Illustrations and Anatomy & Physiology offer high-quality anatomical illustrations.
- Specialized Fitness Websites: Websites focused on fitness and training often feature muscle maps tailored for specific exercise routines.
5. Can muscle maps be used for rehabilitation purposes?
Yes, muscle maps are essential tools for physical therapists and trainers involved in rehabilitation. By understanding the location and function of muscles, therapists can identify the affected muscles, assess the extent of injury, and develop targeted exercises for restoring function and preventing future injuries.
Tips for Utilizing Muscle Maps: Maximizing Their Potential
- Start with basic maps: Begin with simplified muscle maps that highlight major muscle groups, gradually progressing to more detailed illustrations as your understanding deepens.
- Combine visual learning with practical experience: Engage in exercises and activities that involve targeted muscle groups, reinforcing your knowledge through direct experience.
- Utilize interactive resources: Explore online anatomy atlases and interactive muscle maps that allow for three-dimensional visualization and exploration.
- Seek guidance from professionals: Consult with healthcare professionals, fitness trainers, or physical therapists for personalized guidance and interpretation of muscle anatomy.
- Continuously learn and refine your understanding: Stay curious, explore new resources, and strive for ongoing learning to deepen your knowledge of muscle anatomy.
Conclusion: Embracing the Body’s Internal Tapestry
Understanding muscle anatomy through the lens of a muscle map is a journey of discovery, empowering individuals with a deeper appreciation for the body’s incredible capabilities. This knowledge empowers individuals to optimize their physical performance, navigate the complexities of rehabilitation, and gain a profound understanding of their own internal landscape. The muscle map serves as a gateway to unlocking the potential of the human body, fostering a more informed and empowered approach to health, fitness, and movement.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Body’s Internal Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to Muscle Anatomy. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Future: A Deep Dive Into SAP’s Roadmap
- Vanguard: A Comprehensive Exploration Of The Map
- Navigating The African Continent: Understanding Longitude And Latitude
- Unpacking The Geography Of East Europe And Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
- Interstate 5: A Vital Artery Connecting The West Coast
- Navigating Paradise: A Comprehensive Guide To Sandals Resort Locations
- A Coastal Tapestry: Exploring Washington State’s Diverse Shoreline
- Navigating The Beauty Of Utah: A Comprehensive Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply