Unpacking The Geography Of East Europe And Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
Unpacking the Geography of East Europe and Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unpacking the Geography of East Europe and Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unpacking the Geography of East Europe and Russia: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unpacking the Geography of East Europe and Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
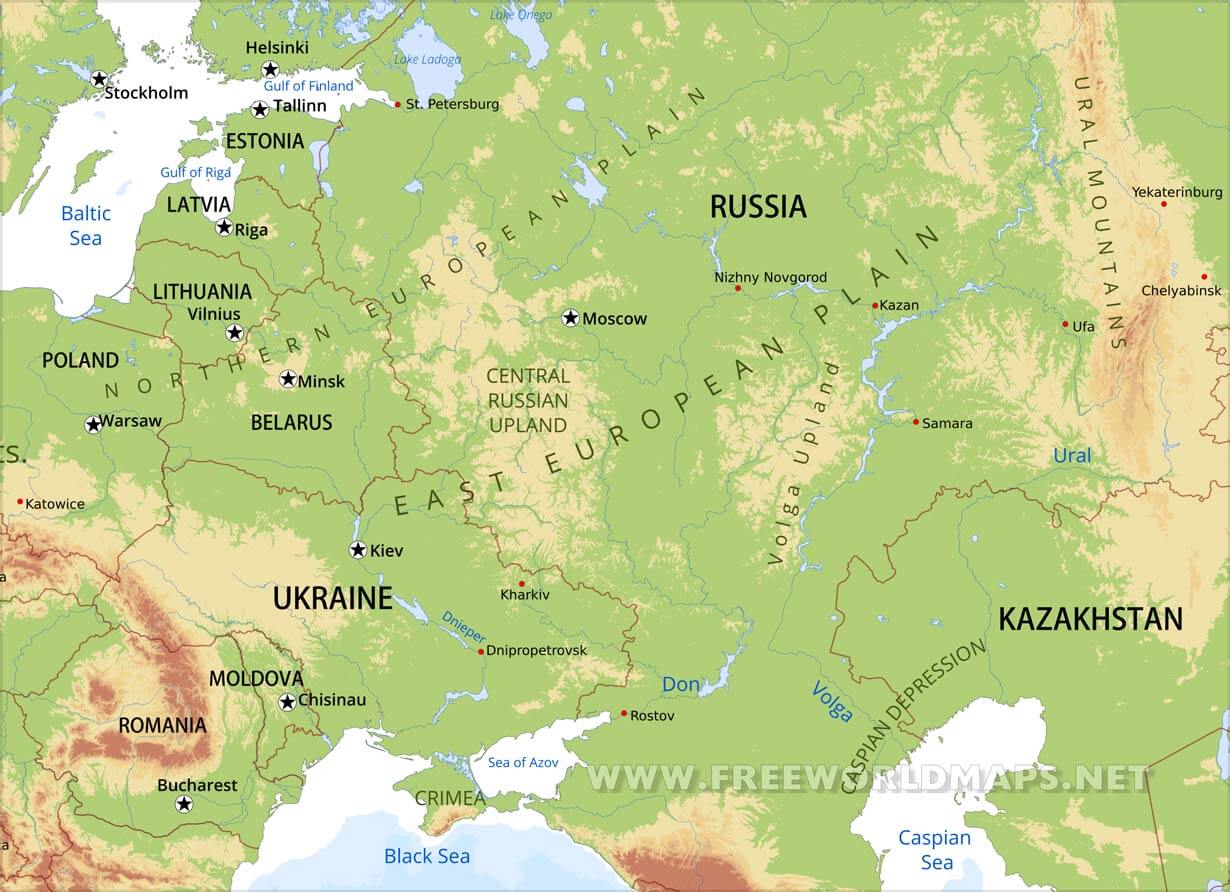
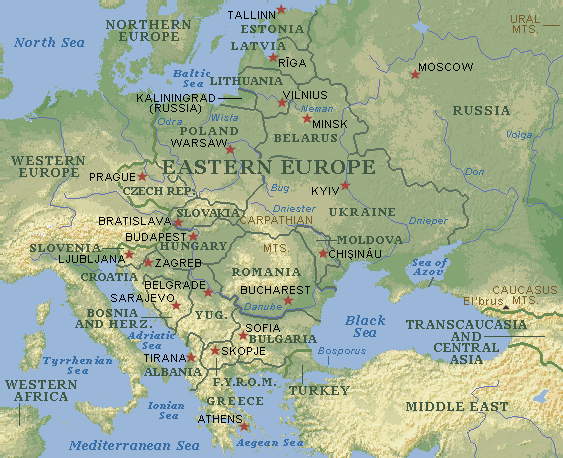
The vast expanse of Eastern Europe and Russia, encompassing a diverse array of landscapes, cultures, and historical experiences, presents a unique challenge for understanding its complex geography. This guide aims to demystify the region’s intricate map, exploring its key features and highlighting the significance of its geographical formations.
Delving into the Topography:
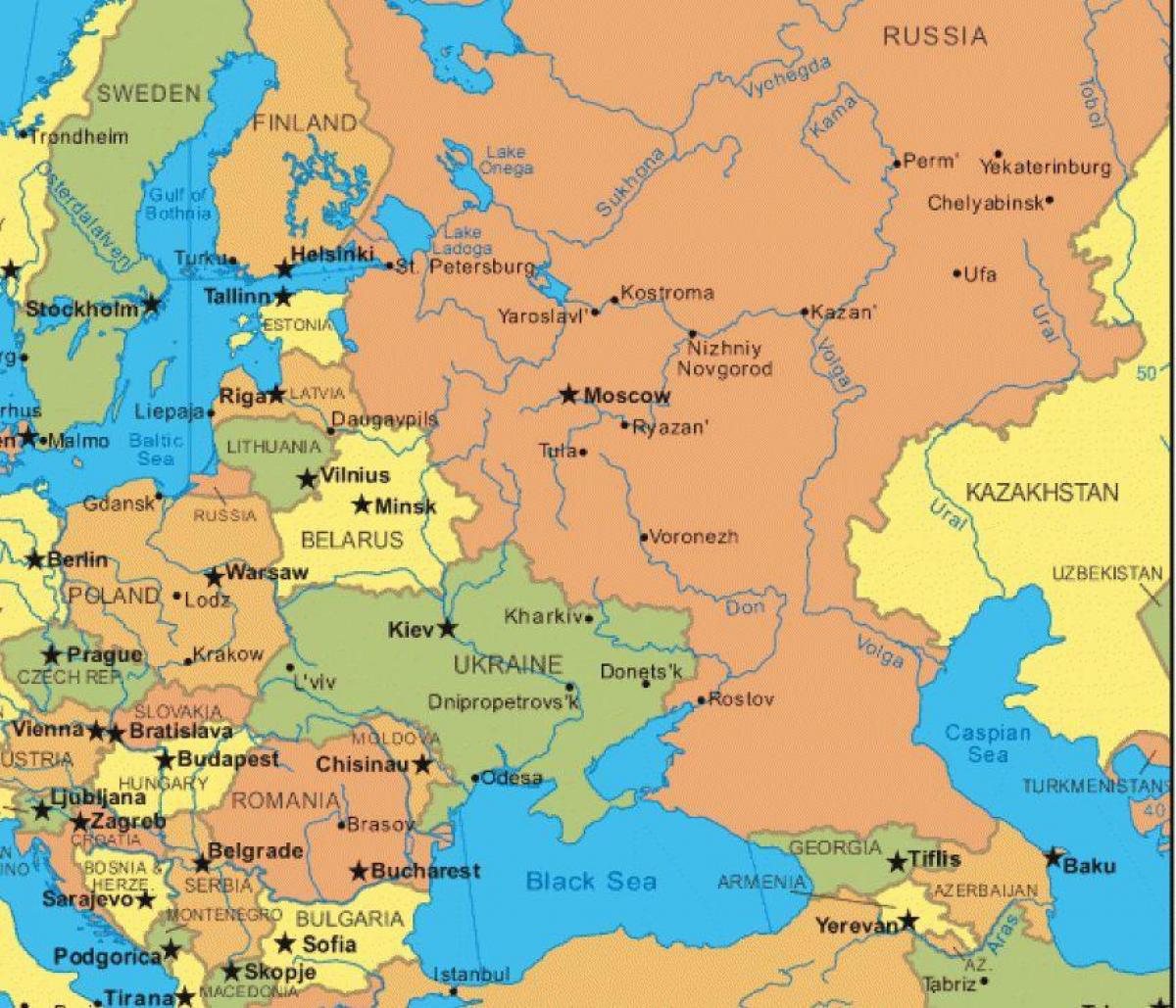
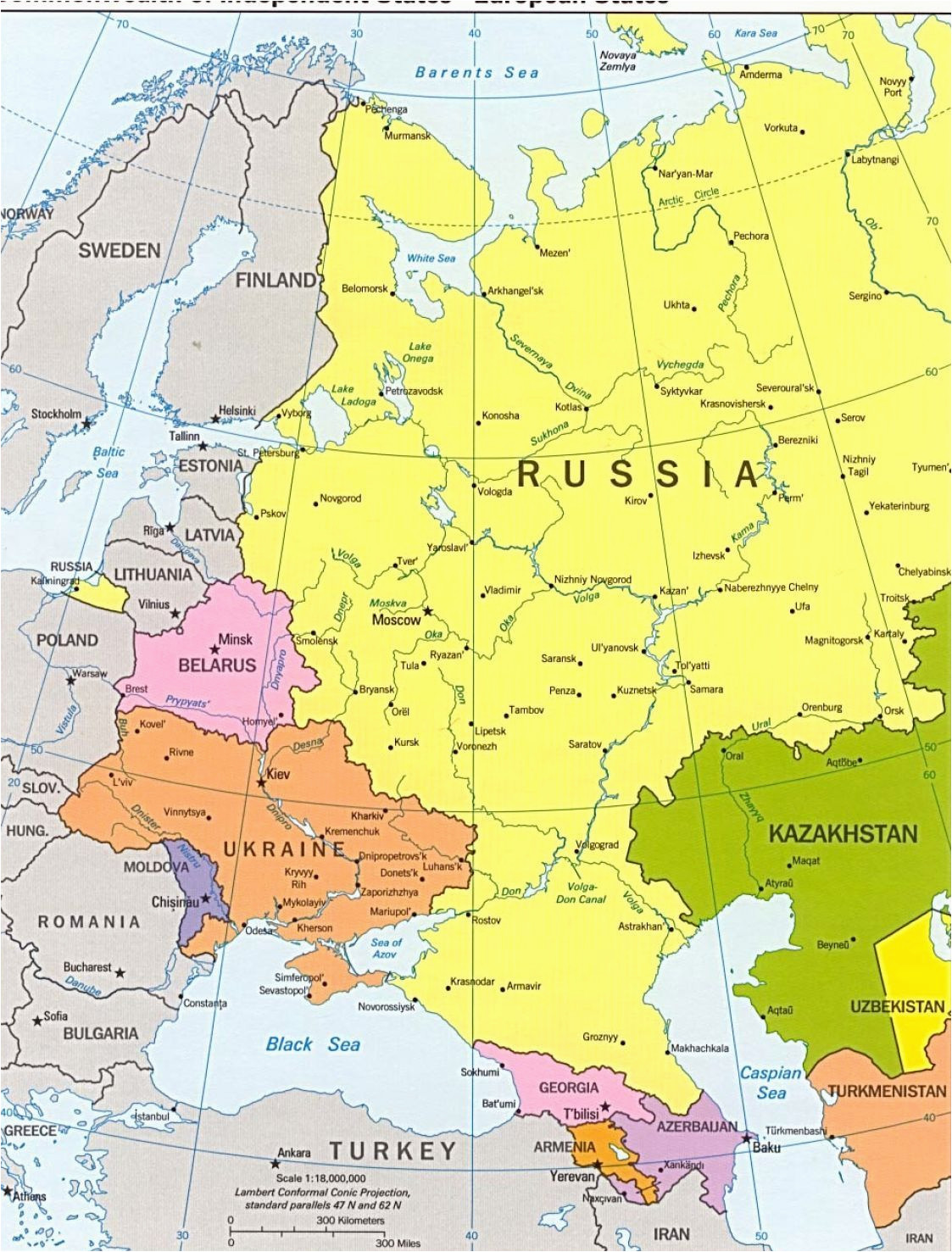
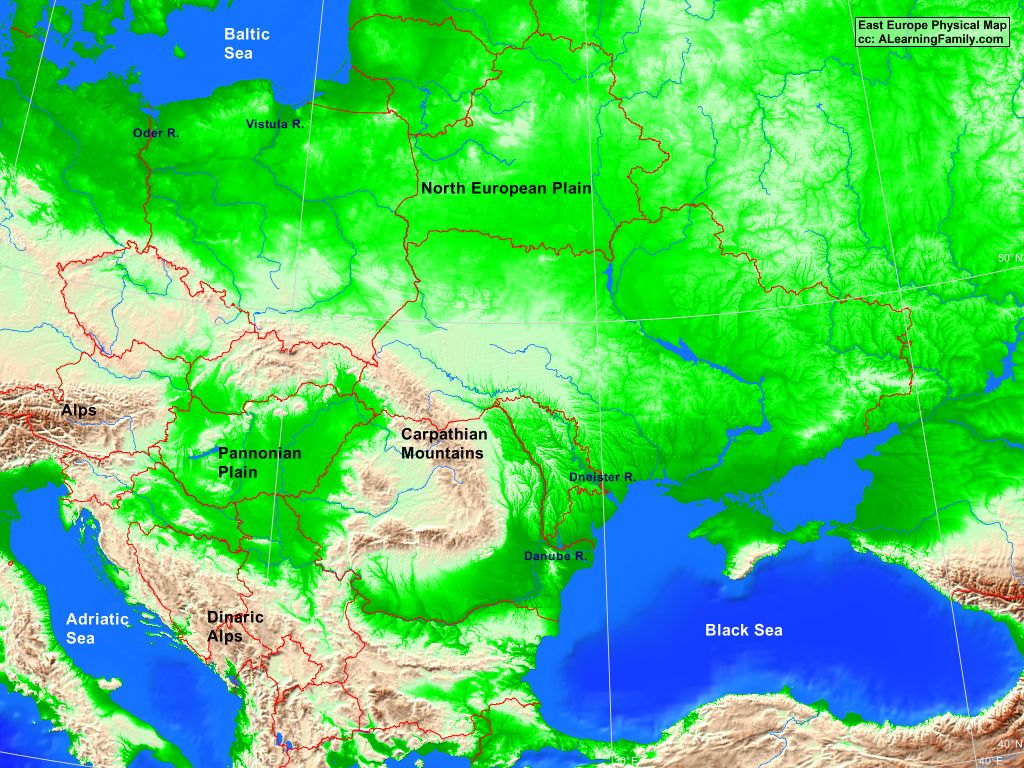
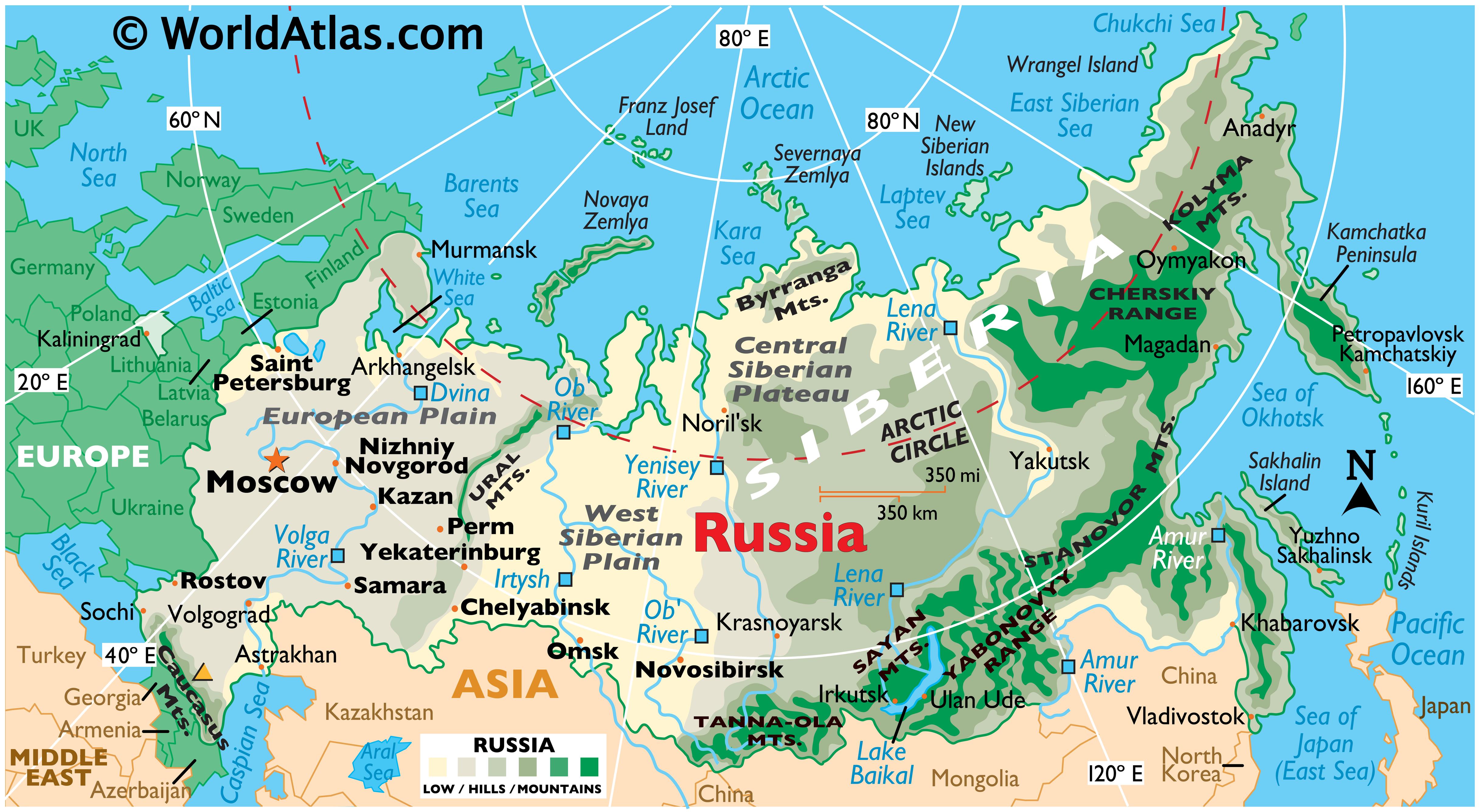
Eastern Europe and Russia are characterized by a dramatic landscape, encompassing vast plains, towering mountains, and sprawling forests. The East European Plain, stretching from the Baltic Sea to the Ural Mountains, forms the region’s heartland, offering fertile land for agriculture and facilitating trade routes. The Ural Mountains, marking the traditional boundary between Europe and Asia, rise dramatically, presenting a natural barrier while also containing rich mineral deposits.
Beyond the plains, the Caucasus Mountains stand as a formidable range, separating the Black Sea from the Caspian Sea. The Carpathian Mountains, curving through Central and Eastern Europe, provide a natural defense against invasion and offer scenic beauty. The Baltic Sea, a vital waterway for trade and maritime activity, borders the northern edge of the region, while the Black Sea, a historical crossroads for civilizations, lies to the south.
Understanding the Political Landscape:
The region’s political map is equally dynamic, reflecting a history of shifting borders and alliances. The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 ushered in a new era of independent states, each with its own unique political and economic systems.
Key Countries:
- Russia: The largest country in the world, spanning eleven time zones and encompassing vast swathes of Siberia, the Caucasus, and the Far East.
- Ukraine: A strategically important country, sharing a lengthy border with Russia and possessing fertile black soil essential for agriculture.
- Belarus: A landlocked country, politically and economically close to Russia, with a significant agricultural sector.
- Poland: A key member of the European Union, bordering both Russia and Germany, and playing a crucial role in regional trade and politics.
- The Baltic States (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania): Small, independent nations with historical ties to Scandinavia, now members of the European Union and NATO.
- The Czech Republic and Slovakia: Two former parts of Czechoslovakia, now independent nations with vibrant economies and strong cultural identities.
- Hungary: A landlocked country with a rich history and a strategic location at the crossroads of Central and Eastern Europe.
- Romania: A country with diverse landscapes, including the Carpathian Mountains and the Danube Delta, and a significant agricultural sector.
- Bulgaria: Located on the Balkan Peninsula, with a long coastline on the Black Sea, and a rich history and culture.
Navigating the Historical Context:
The region’s geography has profoundly shaped its history. The East European Plain, open and accessible, has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, from the Golden Horde to the Soviet Union. The Carpathian Mountains provided refuge for various cultures and ethnicities, while the Black Sea served as a vital trade route for ancient civilizations.
The region’s history is marked by periods of conflict and cooperation. The Cold War, a defining chapter of the 20th century, left a lasting impact on the region’s political landscape and economic development. The fall of the Soviet Union brought about a new era of independence and democratic reforms, but also presented challenges in navigating economic transitions and building stable democracies.
The Significance of Geography:
Understanding the geography of Eastern Europe and Russia is crucial for comprehending the region’s political, economic, and cultural dynamics. The region’s vast natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals, have fueled economic growth and attracted international investment. However, the region’s geography also presents challenges, including a harsh climate, limited access to warm-water ports, and a complex geopolitical landscape.
FAQs about the Geography of Eastern Europe and Russia:
1. What are the major geographical features of Eastern Europe and Russia?
The major geographical features include the East European Plain, the Ural Mountains, the Caucasus Mountains, the Carpathian Mountains, the Baltic Sea, and the Black Sea.
2. How has the geography of the region shaped its history?
The region’s geography has influenced historical developments, including the rise and fall of empires, the migration of peoples, and the course of wars.
3. What are the key political entities within the region?
The key political entities include Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Poland, the Baltic States, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria.
4. What are the major economic activities in the region?
Major economic activities include agriculture, mining, energy production, manufacturing, and tourism.
5. What are some of the challenges facing the region?
Challenges include economic inequality, political instability, environmental degradation, and a complex geopolitical landscape.
Tips for Studying the Geography of Eastern Europe and Russia:
- Use maps and atlases: Visual aids are essential for understanding the region’s physical and political features.
- Explore historical maps: Studying historical maps can provide insights into the region’s changing borders and political dynamics.
- Read about the region’s history: Understanding the historical context is crucial for comprehending the present.
- Engage with cultural resources: Explore the region’s diverse cultures through literature, music, and art.
- Travel to the region: Experiencing the region firsthand can provide invaluable insights into its geography, culture, and people.
Conclusion:
The geography of Eastern Europe and Russia is a tapestry woven with diverse landscapes, complex histories, and dynamic political realities. Understanding the region’s physical and political features is essential for navigating its complexities and appreciating its unique role in the world. By studying the region’s geography, we gain a deeper understanding of its past, present, and future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unpacking the Geography of East Europe and Russia: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Future: A Deep Dive Into SAP’s Roadmap
- Vanguard: A Comprehensive Exploration Of The Map
- Navigating The African Continent: Understanding Longitude And Latitude
- Unpacking The Geography Of East Europe And Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
- Interstate 5: A Vital Artery Connecting The West Coast
- Navigating Paradise: A Comprehensive Guide To Sandals Resort Locations
- A Coastal Tapestry: Exploring Washington State’s Diverse Shoreline
- Navigating The Beauty Of Utah: A Comprehensive Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply