Understanding California’s Precipitation Patterns: A Visual Guide To A Complex Landscape
Understanding California’s Precipitation Patterns: A Visual Guide to a Complex Landscape
Related Articles: Understanding California’s Precipitation Patterns: A Visual Guide to a Complex Landscape
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding California’s Precipitation Patterns: A Visual Guide to a Complex Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding California’s Precipitation Patterns: A Visual Guide to a Complex Landscape

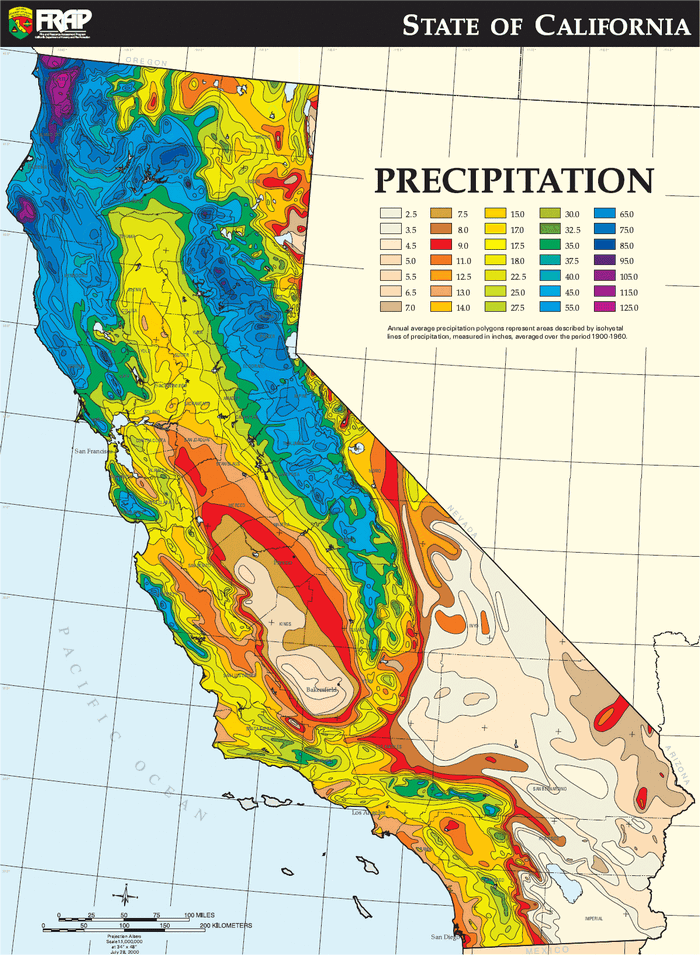
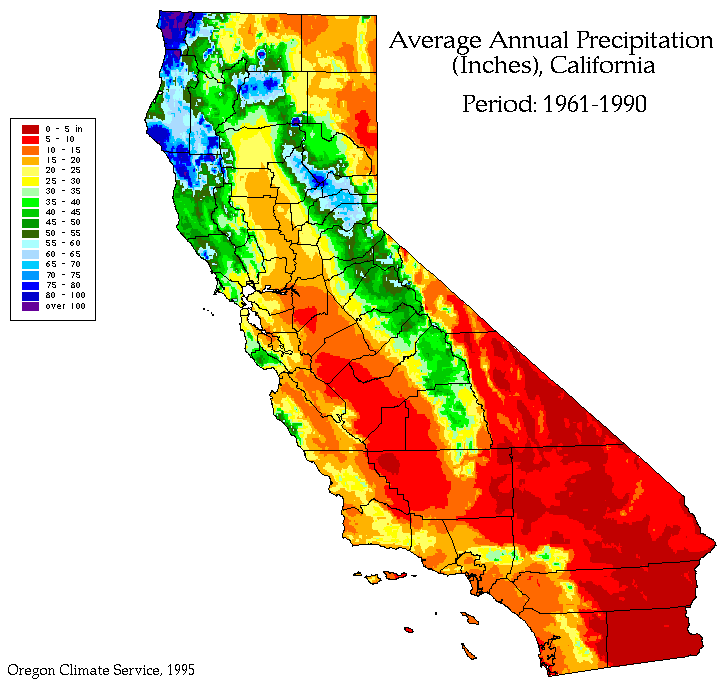
California, a state renowned for its diverse landscapes and vibrant ecosystems, is also a region characterized by stark contrasts in precipitation. From the lush forests of the north to the arid deserts of the south, the state experiences a wide range of rainfall patterns, making it crucial to understand the distribution of water resources for effective management and planning. A visual representation of this complex precipitation landscape is provided by California precipitation maps.
Deciphering the Depiction: A Look at California Precipitation Maps
California precipitation maps are graphical representations of the average annual rainfall across the state. They typically utilize color gradients or contour lines to illustrate variations in precipitation levels, with darker shades or higher contour values indicating areas with higher rainfall. These maps offer a valuable overview of the spatial distribution of precipitation, allowing for a deeper understanding of regional differences and the factors that influence them.
Factors Shaping California’s Rainfall
Several factors contribute to the diverse precipitation patterns observed across California:
- Latitude: California’s vast north-south expanse places different regions under varying atmospheric conditions. The northern regions receive more rainfall than the southern regions due to the influence of the Pacific Ocean and prevailing westerly winds.
- Orographic Effect: The state’s mountainous terrain significantly impacts rainfall distribution. As moist air masses from the Pacific Ocean encounter mountain ranges, they are forced upward, leading to condensation and precipitation on the windward slopes. The leeward slopes, shielded from the moisture, receive less rainfall, creating a rain shadow effect.
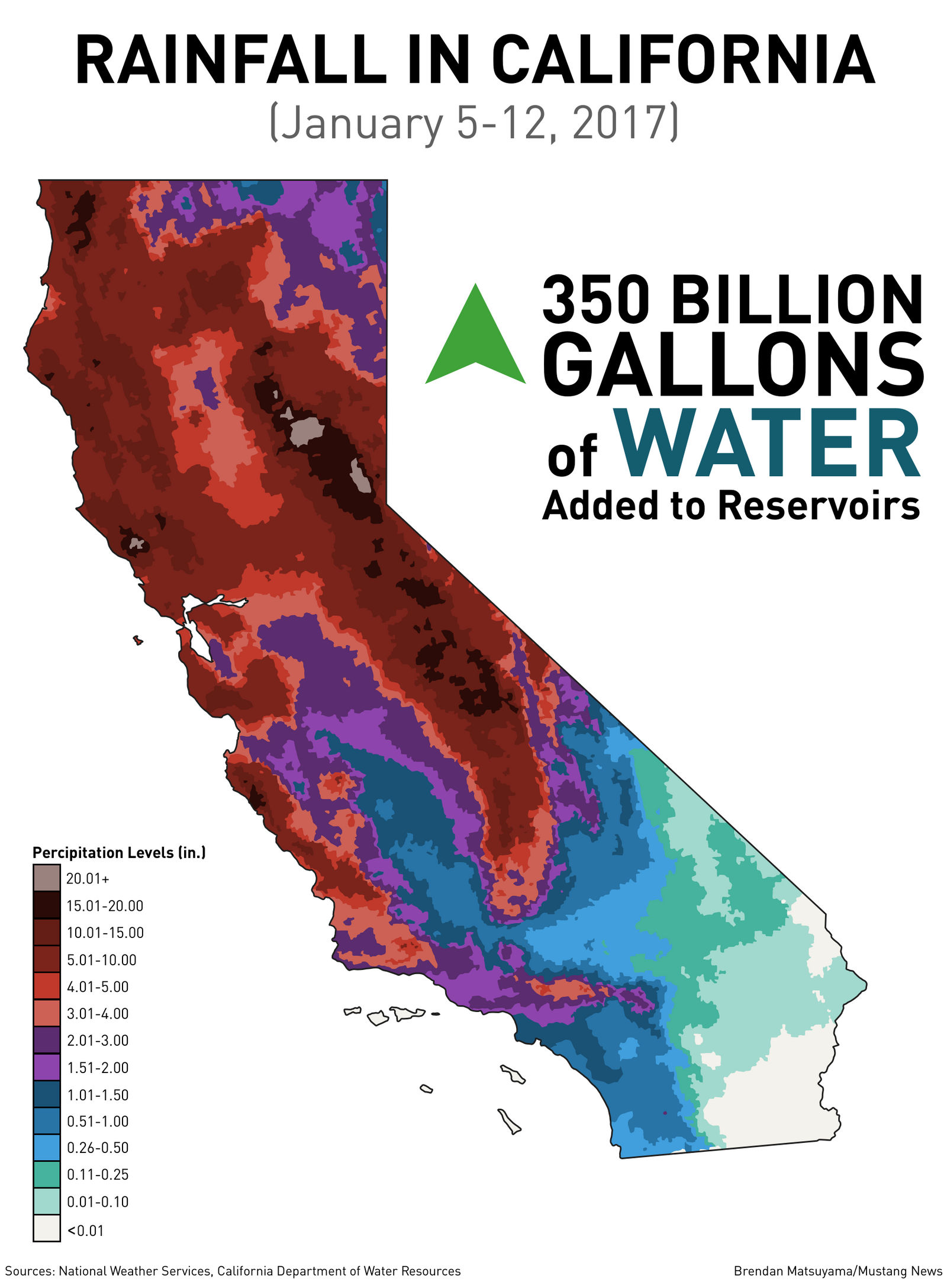
- El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO): This cyclical climate pattern significantly influences California’s rainfall. During El Niño years, warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central Pacific Ocean lead to increased precipitation in California, particularly in the northern and central regions. Conversely, La Niña years, characterized by cooler sea surface temperatures, often result in drier conditions.
- Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO): This long-term climate pattern, with cycles lasting 20-30 years, also affects California’s precipitation. Positive PDO phases are associated with increased rainfall, while negative phases lead to drier conditions.
The Importance of California Precipitation Maps
California precipitation maps serve as essential tools for various purposes:
- Water Resource Management: Understanding the spatial distribution of rainfall allows for efficient management of water resources. By identifying areas with higher precipitation, water agencies can develop strategies for collecting and storing water, ensuring sufficient supply for urban, agricultural, and environmental needs.
- Drought Prediction and Mitigation: Precipitation maps provide valuable insights into drought patterns, helping authorities anticipate and mitigate potential water shortages. They allow for the development of drought contingency plans and the implementation of conservation measures to minimize the impact of dry periods.
- Agricultural Planning: Farmers rely on these maps to understand the rainfall patterns in their regions, allowing them to select appropriate crops and implement irrigation strategies based on water availability.
- Ecosystem Management: Precipitation maps are crucial for understanding the water needs of various ecosystems, including forests, grasslands, and wetlands. They help in identifying areas susceptible to drought or flooding, guiding conservation efforts and ensuring the health of these critical habitats.
- Climate Change Research: Analyzing long-term precipitation data from maps provides insights into the changing rainfall patterns, enabling scientists to study the impacts of climate change on California’s water resources and ecosystems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about California Precipitation Maps
Q: What is the average annual precipitation in California?
A: The average annual precipitation in California varies significantly across the state. The northern regions receive an average of 30-50 inches of rainfall annually, while the southern regions receive less than 10 inches.
Q: How are California precipitation maps created?
A: These maps are typically created by analyzing long-term rainfall data collected from weather stations across the state. The data is then processed and interpolated to create a spatial representation of precipitation patterns.
Q: What are the limitations of California precipitation maps?
A: Precipitation maps represent average rainfall patterns, not the actual rainfall experienced in any given year. They do not account for localized variations in precipitation due to factors like topography and microclimates. Additionally, they do not capture the intensity and frequency of rainfall events.
Q: Where can I access California precipitation maps?
A: Various organizations, including the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the California Department of Water Resources, and the University of California Cooperative Extension, provide online access to precipitation maps and data.
Tips for Understanding and Using California Precipitation Maps
- Consider the Timeframe: Precipitation maps typically depict average annual rainfall. To understand current conditions, consult recent rainfall data or weather reports.
- Pay Attention to Scale: The scale of the map influences the level of detail. Larger-scale maps provide more localized information, while smaller-scale maps offer a broader overview.
- Interpret Color Gradients: Understand the color scheme used to represent precipitation levels, ensuring accurate interpretation of the data.
- Combine with Other Data: Utilize precipitation maps in conjunction with other relevant data, such as elevation maps, vegetation maps, and soil maps, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the region.
Conclusion
California precipitation maps offer a valuable visual representation of the state’s diverse rainfall patterns. By understanding the factors influencing precipitation and the information provided by these maps, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions regarding water resource management, drought preparedness, agricultural planning, ecosystem conservation, and climate change adaptation. These maps serve as vital tools for navigating the complexities of California’s water resources and ensuring the sustainability of its unique environment.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding California’s Precipitation Patterns: A Visual Guide to a Complex Landscape. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Future: A Deep Dive Into SAP’s Roadmap
- Vanguard: A Comprehensive Exploration Of The Map
- Navigating The African Continent: Understanding Longitude And Latitude
- Unpacking The Geography Of East Europe And Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
- Interstate 5: A Vital Artery Connecting The West Coast
- Navigating Paradise: A Comprehensive Guide To Sandals Resort Locations
- A Coastal Tapestry: Exploring Washington State’s Diverse Shoreline
- Navigating The Beauty Of Utah: A Comprehensive Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply