The Power Of Maps: Navigating The World Of Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
The Power of Maps: Navigating the World of Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Related Articles: The Power of Maps: Navigating the World of Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Power of Maps: Navigating the World of Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Maps: Navigating the World of Geographic Information Systems (GIS)

Geographic information systems (GIS) have revolutionized the way we understand and interact with the world. At the heart of this technology lies the map, a powerful tool for visualizing, analyzing, and communicating spatial data. This article explores the fundamental principles of GIS maps, delving into their construction, applications, and immense value across various disciplines.
Understanding the Building Blocks of GIS Maps
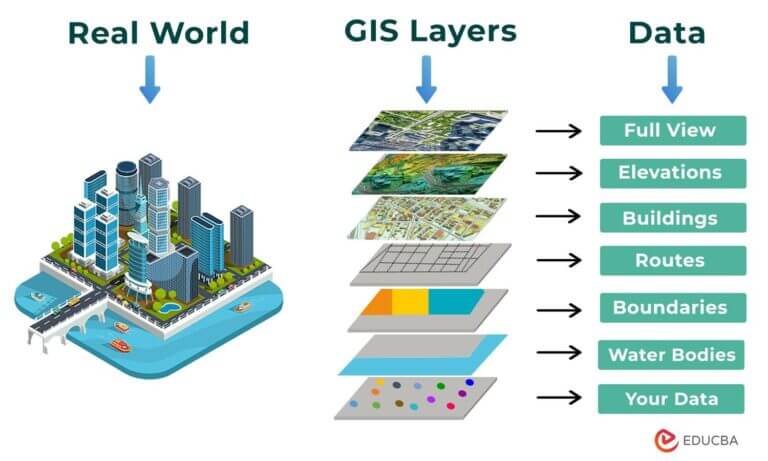
GIS maps are not merely static representations of geographical features. They are dynamic and interactive tools that integrate data from various sources, allowing for sophisticated analysis and visualization. Key components of a GIS map include:
- Geographic Data: This forms the foundation of a GIS map, encompassing information about locations, features, and attributes. Data sources can range from satellite imagery and aerial photographs to census records and environmental monitoring data.
- Spatial Data Models: GIS maps rely on specific models to represent geographical information. Common models include vector data (points, lines, and polygons) and raster data (gridded data representing continuous phenomena like elevation or temperature).
- Map Projections: The Earth’s curved surface needs to be transformed into a flat map, which necessitates the use of projections. Different projections distort geographical distances and shapes in different ways, influencing map accuracy and interpretation.
- Symbology and Visualization: GIS maps employ visual elements like colors, symbols, and patterns to represent data and convey meaning. Effective symbology is crucial for clear communication and effective data analysis.
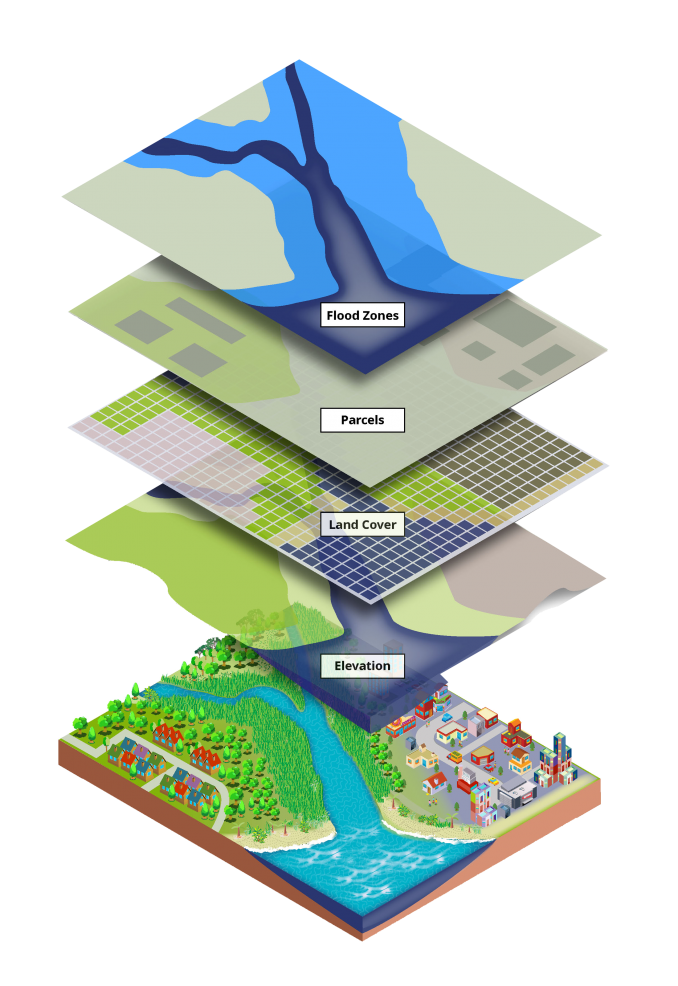
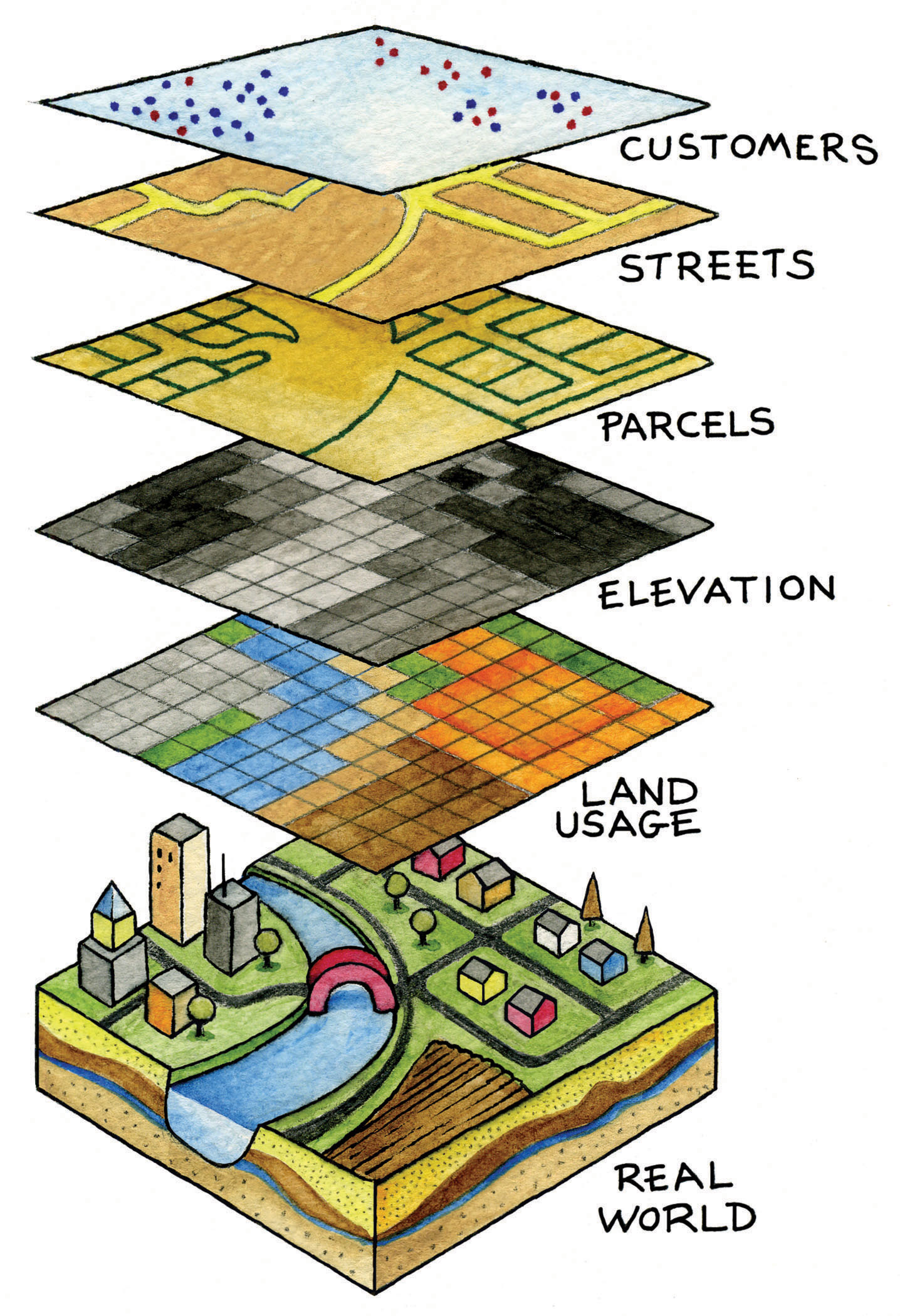
- Layers and Data Integration: GIS maps allow for the overlaying of multiple data layers, enabling users to analyze relationships and patterns across different datasets. This capability is particularly valuable for understanding complex spatial phenomena.
Applications of GIS Maps: Transforming Industries and Decision-Making
The versatility of GIS maps has made them indispensable tools across a wide range of fields, influencing decision-making and driving innovation. Some key applications include:
- Urban Planning and Development: GIS maps assist in analyzing population density, transportation networks, and land use patterns, guiding urban planning initiatives for sustainable growth and efficient infrastructure development.
- Environmental Management: GIS maps enable the monitoring of environmental conditions, identifying pollution sources, tracking deforestation, and assessing the impact of climate change, facilitating informed environmental policy and conservation efforts.
- Disaster Management: GIS maps play a crucial role in disaster preparedness and response. They help visualize hazard zones, track the spread of wildfires or floods, and coordinate emergency response efforts.
- Resource Management: GIS maps aid in managing natural resources like water, minerals, and forests. They assist in optimizing resource extraction, identifying sustainable harvesting practices, and protecting vulnerable ecosystems.
- Transportation and Logistics: GIS maps are essential for optimizing transportation routes, managing traffic flow, and planning efficient logistics networks, contributing to cost savings and improved delivery times.
- Public Health: GIS maps facilitate disease surveillance, identifying disease hotspots, and tracking the spread of infectious diseases, enabling public health officials to prioritize interventions and contain outbreaks.
- Business and Marketing: GIS maps aid in market analysis, identifying customer demographics, optimizing store locations, and analyzing market trends, providing businesses with valuable insights for strategic decision-making.
Benefits of GIS Maps: Empowering Knowledge and Action
The utilization of GIS maps offers significant advantages, empowering individuals and organizations to:
- Visualize and Understand Spatial Data: GIS maps provide a powerful visual representation of complex spatial data, making it easier to understand relationships, patterns, and trends.
- Analyze Data and Identify Trends: GIS maps facilitate the analysis of spatial data, enabling the identification of correlations, patterns, and anomalies, leading to informed decision-making.
- Communicate Information Effectively: GIS maps provide a clear and concise way to communicate spatial information to stakeholders, fostering collaboration and understanding.
- Solve Problems and Make Informed Decisions: GIS maps empower users to identify solutions to spatial problems, optimize resource allocation, and make informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
- Promote Transparency and Accountability: GIS maps can enhance transparency and accountability by providing readily accessible spatial data and analysis, fostering public trust and informed participation.
FAQs about GIS Maps
Q: What are the different types of GIS maps?
A: GIS maps encompass a wide range of types, including thematic maps (highlighting specific themes like population density or land cover), reference maps (providing general geographical information), and choropleth maps (using color gradients to represent data values).
Q: How can I create a GIS map?
A: Creating a GIS map requires specialized software like ArcGIS, QGIS, or MapInfo. These programs allow users to import data, define map projections, choose symbology, and create interactive maps.
Q: What are the limitations of GIS maps?
A: GIS maps rely on data accuracy and completeness. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misleading interpretations. Additionally, GIS maps are subject to limitations imposed by map projections and the inherent complexity of representing the three-dimensional Earth on a two-dimensional surface.
Q: What are the future trends in GIS mapping?
A: The future of GIS mapping is intertwined with advancements in technology, including artificial intelligence (AI), big data analysis, and cloud computing. These advancements are expected to lead to more sophisticated map functionalities, real-time data integration, and personalized mapping experiences.
Tips for Effective GIS Mapping
- Start with a clear purpose: Define the specific objective of your map to guide data selection, map design, and analysis.
- Choose the right data: Select data sources that are relevant to your objective and of sufficient quality and accuracy.
- Consider map projections: Select a projection that minimizes distortion for your specific area of interest and purpose.
- Use effective symbology: Employ clear and consistent symbology to convey information effectively and avoid ambiguity.
- Test and validate your map: Ensure your map accurately represents the data and meets your analytical needs.
- Communicate your findings: Present your map in a clear and concise manner, highlighting key findings and insights.
Conclusion: The Future of GIS Maps and Spatial Intelligence
GIS maps have become essential tools for understanding and interacting with the world. Their ability to visualize, analyze, and communicate spatial data has transformed decision-making across diverse fields. As technology continues to evolve, GIS maps are poised to play an even more prominent role in shaping our understanding of the world and driving sustainable solutions for the future. By leveraging the power of spatial intelligence, we can unlock new possibilities for innovation, progress, and a more informed and sustainable world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Maps: Navigating the World of Geographic Information Systems (GIS). We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Future: A Deep Dive Into SAP’s Roadmap
- Vanguard: A Comprehensive Exploration Of The Map
- Navigating The African Continent: Understanding Longitude And Latitude
- Unpacking The Geography Of East Europe And Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
- Interstate 5: A Vital Artery Connecting The West Coast
- Navigating Paradise: A Comprehensive Guide To Sandals Resort Locations
- A Coastal Tapestry: Exploring Washington State’s Diverse Shoreline
- Navigating The Beauty Of Utah: A Comprehensive Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply