The Nile’s Embrace: Understanding The Geography Of Lower And Upper Egypt
The Nile’s Embrace: Understanding the Geography of Lower and Upper Egypt
Related Articles: The Nile’s Embrace: Understanding the Geography of Lower and Upper Egypt
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Nile’s Embrace: Understanding the Geography of Lower and Upper Egypt. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Nile’s Embrace: Understanding the Geography of Lower and Upper Egypt
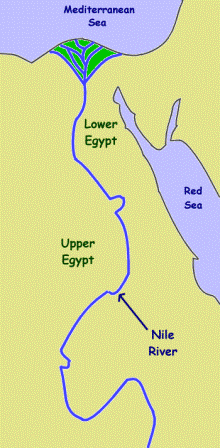
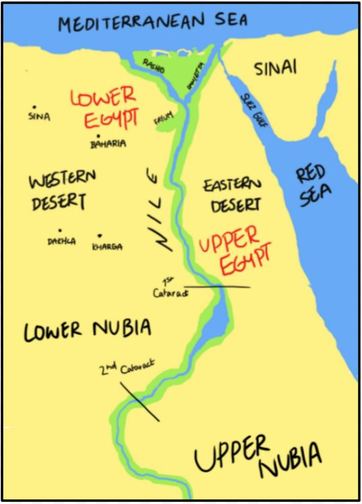
The Nile River, a lifeblood coursing through the heart of Egypt, has not only shaped the land but also defined its history and culture. Its flow, from south to north, naturally divided the country into two distinct regions: Upper Egypt, the source of the Nile’s journey, and Lower Egypt, where the river reaches the Mediterranean Sea. This division, while seemingly simple, holds profound implications for understanding the complexities of ancient and modern Egypt.
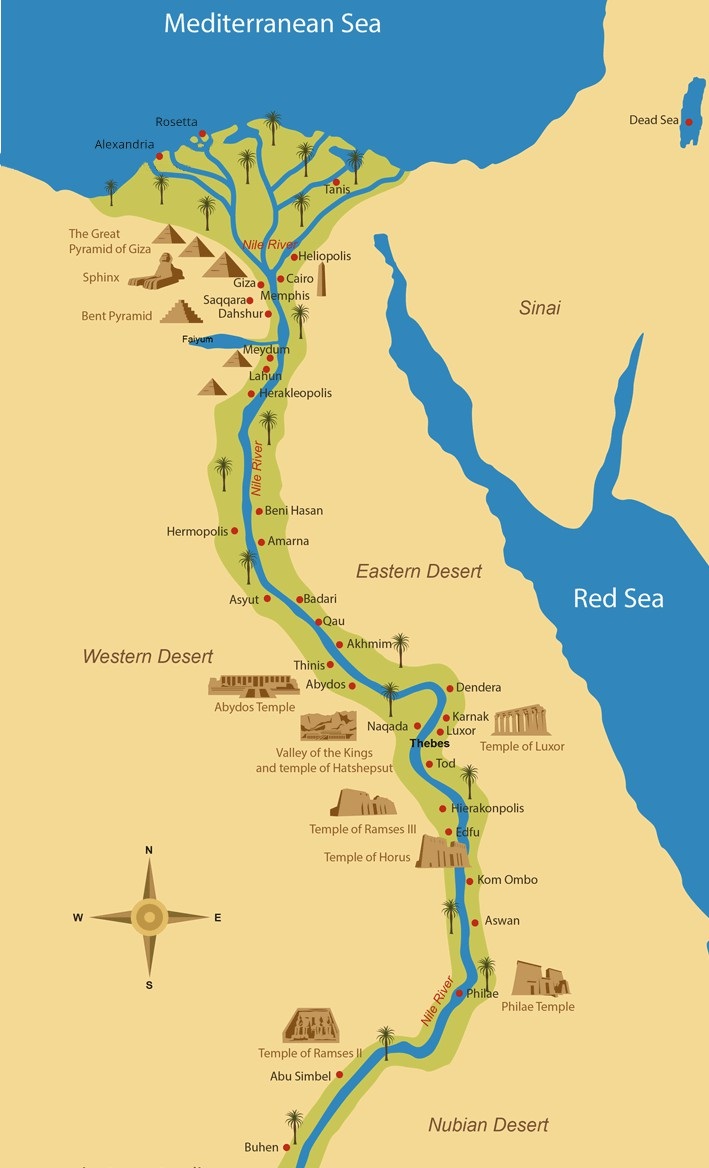
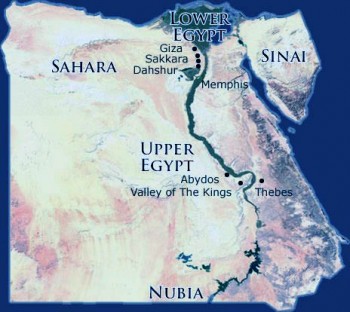
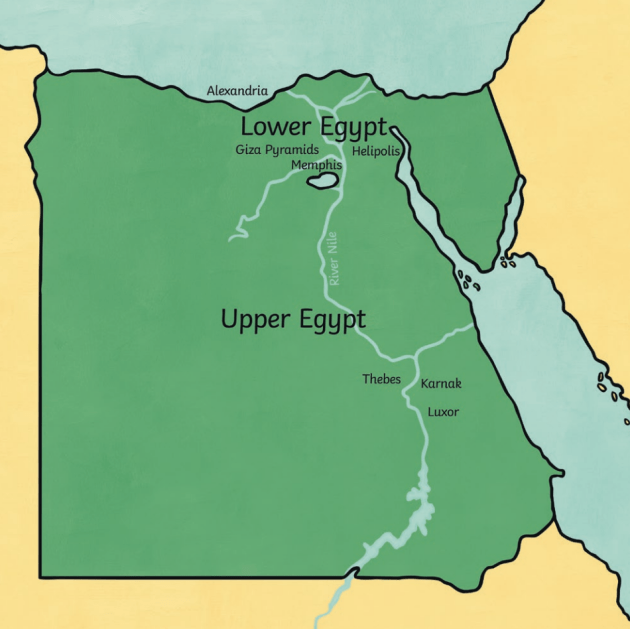
Upper Egypt: The Source of Civilization
Located south of Cairo, Upper Egypt stretches towards the First Cataract, a dramatic rock formation marking the southern limit of the Nile’s navigable waters. This region, often referred to as "The Land of the South," is characterized by its arid landscape, punctuated by fertile oases and the dramatic cliffs of the Eastern and Western Deserts.
The Upper Egyptian landscape was, and still is, dominated by the Nile’s presence. Its fertile banks were the cradle of ancient Egyptian civilization, providing fertile land for agriculture and a natural highway for trade and communication. The region witnessed the rise and fall of numerous pharaonic dynasties, each leaving behind monumental testaments to their power – the towering temples of Karnak and Luxor, the enigmatic tombs of the Valley of the Kings, and the colossal statues of Abu Simbel.
Lower Egypt: The Delta and the Mediterranean
Lower Egypt, the "Land of the North," encompasses the Nile Delta, a vast alluvial plain formed by the river’s sediment as it approaches the Mediterranean Sea. This fertile region, with its network of canals and waterways, provided a rich agricultural base for ancient Egypt, supporting a dense population and thriving cities.
The Nile Delta was also a critical hub for trade, connecting Egypt with the wider Mediterranean world. Its strategic location facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures, shaping the development of Egyptian society. The region’s rich history is reflected in the majestic pyramids of Giza, the bustling port city of Alexandria, and the ruins of ancient cities like Sais and Tanis.
The Significance of the Division
The division between Lower and Upper Egypt, while geographically defined, has profound cultural and historical significance.
- Political and Administrative Structure: The two regions were often governed separately, with distinct political entities and administrative structures. This division was particularly evident during the Old Kingdom period, when Upper Egypt was ruled by the pharaohs while Lower Egypt was controlled by a separate, powerful nomarch (governor).
- Cultural Identity: The two regions developed distinct cultural identities, reflected in their art, religion, and social customs. The iconic "White Crown" of Upper Egypt, symbolic of power and authority, differed from the "Red Crown" of Lower Egypt, representing the strength and vitality of the Delta.
- Economic Interdependence: Despite their differences, Lower and Upper Egypt were inextricably linked by the Nile, fostering economic interdependence. Upper Egypt provided agricultural produce, while Lower Egypt offered access to trade routes and the vital resources of the Mediterranean Sea.
The Enduring Legacy
The division between Lower and Upper Egypt, though a product of the Nile’s geography, has left an enduring mark on Egyptian history and culture. It continues to influence the country’s political landscape, economic development, and cultural identity. Understanding this division is crucial for comprehending the complexities of Egyptian society, past and present.
FAQs
Q: What are the key geographical features of Lower and Upper Egypt?
A: Upper Egypt is characterized by its arid landscape, dominated by the Nile River and punctuated by oases and desert cliffs. Lower Egypt is defined by the Nile Delta, a fertile alluvial plain formed by the river’s sediment, and its access to the Mediterranean Sea.
Q: What are the historical differences between Lower and Upper Egypt?
A: Upper Egypt was the birthplace of ancient Egyptian civilization, witnessing the rise and fall of numerous pharaonic dynasties and the construction of monumental temples and tombs. Lower Egypt was a major hub for trade and cultural exchange, with its own distinct political and administrative structures.
Q: How did the division between Lower and Upper Egypt impact the development of Egyptian culture?
A: The two regions developed distinct cultural identities, reflected in their art, religion, and social customs. The division also shaped the political landscape, influencing the rise and fall of various dynasties and the evolution of governance structures.
Q: What is the significance of the division between Lower and Upper Egypt today?
A: The division continues to influence the country’s political landscape, economic development, and cultural identity. Understanding the historical and cultural differences between the two regions is crucial for comprehending the complexities of modern Egypt.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Lower and Upper Egypt
- Focus on the Nile River: The river’s flow is the defining element of the map, determining the boundaries of the two regions and influencing their development.
- Explore the major cities and landmarks: Understanding the location of key cities like Cairo, Alexandria, Luxor, and Aswan provides insight into the historical and cultural significance of each region.
- Consider the geographic features: The arid landscape of Upper Egypt and the fertile delta of Lower Egypt are crucial elements in shaping the character of each region.
Conclusion
The map of Lower and Upper Egypt is more than a geographical representation; it is a visual testament to the enduring power of the Nile River and its influence on Egyptian civilization. Understanding this division, with its historical and cultural significance, is key to appreciating the complexity and richness of Egypt’s past and present. By studying the map, we gain valuable insights into the nation’s development, its cultural heritage, and its enduring connection to the river that has shaped its destiny.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Nile’s Embrace: Understanding the Geography of Lower and Upper Egypt. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Future: A Deep Dive Into SAP’s Roadmap
- Vanguard: A Comprehensive Exploration Of The Map
- Navigating The African Continent: Understanding Longitude And Latitude
- Unpacking The Geography Of East Europe And Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
- Interstate 5: A Vital Artery Connecting The West Coast
- Navigating Paradise: A Comprehensive Guide To Sandals Resort Locations
- A Coastal Tapestry: Exploring Washington State’s Diverse Shoreline
- Navigating The Beauty Of Utah: A Comprehensive Guide To Printable Maps

Leave a Reply