The Andes Mountains: A Continental Backbone And A Tapestry Of Life
The Andes Mountains: A Continental Backbone and a Tapestry of Life
Related Articles: The Andes Mountains: A Continental Backbone and a Tapestry of Life
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Andes Mountains: A Continental Backbone and a Tapestry of Life. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Andes Mountains: A Continental Backbone and a Tapestry of Life

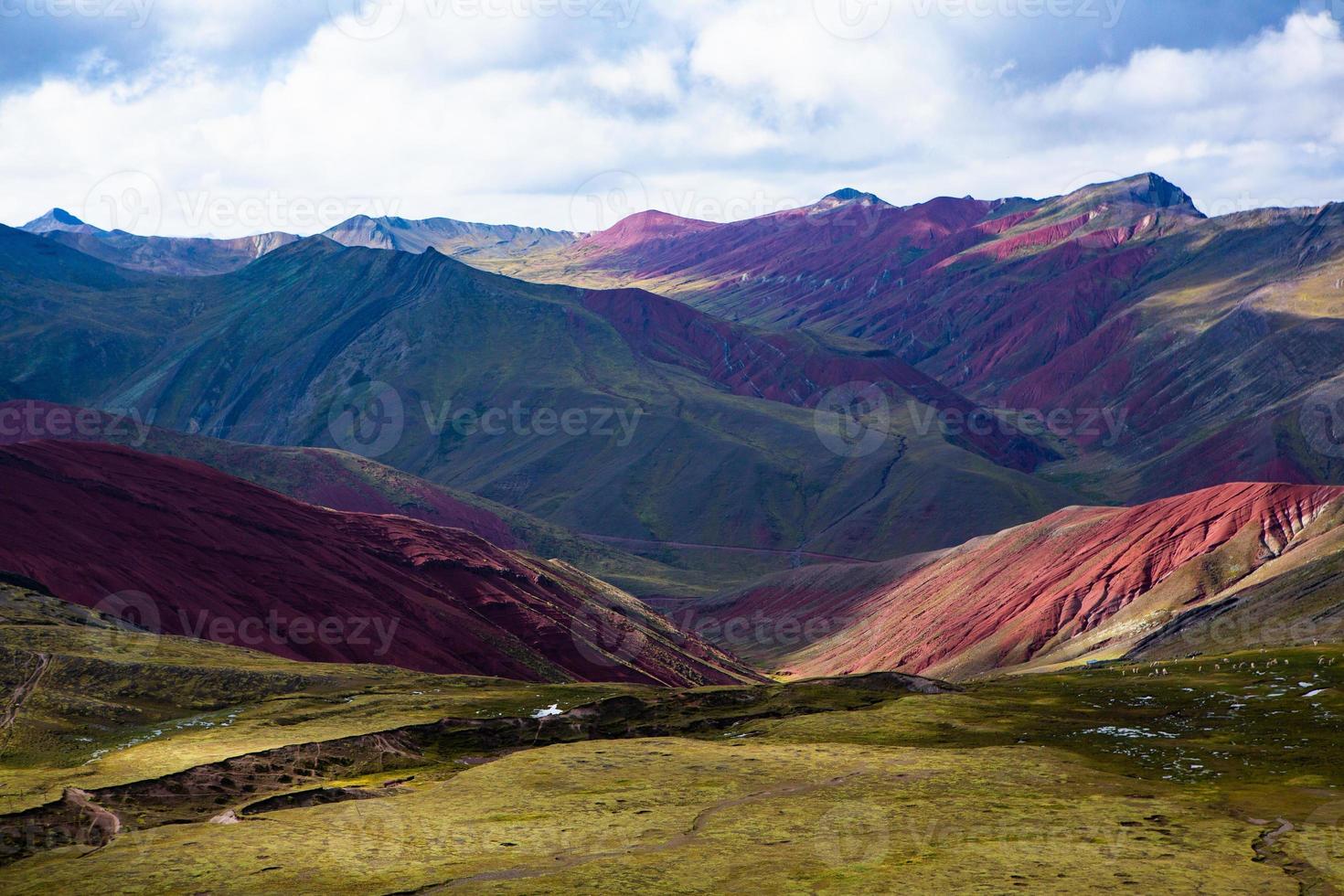
The Andes Mountains, a formidable spine stretching along the western edge of South America, are a testament to the Earth’s dynamic processes and a crucible for biodiversity. This colossal mountain range, second only to the Himalayas in terms of average elevation, shapes the landscapes, climates, and ecosystems of seven South American nations. Understanding the Andes through a map reveals its intricate geography, profound ecological importance, and rich cultural heritage.
A Geographical Tapestry:
An Andes Mountains map is a visual representation of the range’s remarkable geographic diversity. It showcases the different sections of the Andes, each with its unique characteristics:
- Northern Andes: This section begins in Venezuela and Colombia, marked by a series of parallel ranges, including the Cordillera Occidental, Cordillera Central, and Cordillera Oriental. It is home to the highest peak in Venezuela, Pico Bolívar, and boasts a diverse landscape of cloud forests, páramos, and Andean valleys.
- Central Andes: Extending across Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia, this section features the highest peaks in the Andes, including Mount Huascarán in Peru and Mount Aconcagua in Argentina. It is characterized by a rugged terrain of high plateaus, deep canyons, and towering volcanoes, such as the active Cotopaxi in Ecuador.
- Southern Andes: Spanning Chile and Argentina, this section is marked by a more gradual decrease in elevation. It includes the Patagonian Andes, a region of glaciated mountains, vast lakes, and towering peaks like Mount Fitz Roy.
The Andes on the Map: Unveiling the Importance
Beyond its physical grandeur, the Andes Mountains map unveils the range’s profound importance in shaping South America’s landscape, climate, and human history:
- Biodiversity Hotspot: The Andes are a global biodiversity hotspot, harboring an astonishing array of flora and fauna. The map reveals the intricate mosaic of ecosystems, from the lush rainforests of the eastern slopes to the high-altitude páramos, home to unique plant and animal species adapted to harsh conditions. This rich biodiversity is crucial for ecosystem services, such as water regulation and carbon sequestration.
- Water Tower of South America: The Andes act as a vast water tower, providing water resources to millions of people in South America. The map highlights the numerous rivers that originate in the Andes, including the Amazon, Orinoco, and Paraná, which contribute to the continent’s vast river systems. The glaciers in the Andes also act as important reservoirs of freshwater, a resource increasingly threatened by climate change.
- Cultural Crossroads: The Andes Mountains have been a cradle of civilization for millennia. The map reveals the ancient Inca Empire’s influence, stretching across the central Andes, with its iconic cities like Machu Picchu and Cuzco. The Andes continue to be a vibrant cultural landscape, with indigenous communities maintaining their traditions and languages, contributing to the region’s rich cultural tapestry.
FAQs About the Andes Mountains Map:
- What is the highest peak in the Andes? Mount Aconcagua in Argentina, with an elevation of 6,961 meters (22,838 feet).
- What are the main ecosystems found in the Andes? The Andes encompass a wide range of ecosystems, including tropical rainforests, cloud forests, páramos, grasslands, and deserts.
- What is the impact of climate change on the Andes? Climate change is causing glaciers in the Andes to melt at an alarming rate, affecting water resources and posing risks to downstream communities.
Tips for Understanding the Andes Mountains Map:
- Pay attention to elevation: The map’s elevation contours highlight the dramatic changes in altitude, revealing the different ecosystems and human settlements found in the Andes.
- Study the major rivers: Tracing the course of major rivers on the map provides insight into the water resources and their importance for human life and ecosystems.
- Explore the cultural heritage: The map can guide you to ancient ruins, indigenous communities, and cultural sites, showcasing the rich history and traditions of the Andes.
Conclusion:
The Andes Mountains map is more than just a geographical representation; it is a window into a world of biodiversity, cultural heritage, and environmental challenges. Understanding the Andes through a map enables us to appreciate its role as a vital ecosystem, a source of life-giving resources, and a testament to the resilience of human civilizations. By studying the Andes Mountains map, we gain a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of nature, culture, and human well-being, fostering a greater appreciation for this majestic mountain range and its importance for the planet.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Andes Mountains: A Continental Backbone and a Tapestry of Life. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Future: A Deep Dive Into SAP’s Roadmap
- Vanguard: A Comprehensive Exploration Of The Map
- Navigating The African Continent: Understanding Longitude And Latitude
- Unpacking The Geography Of East Europe And Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
- Interstate 5: A Vital Artery Connecting The West Coast
- Navigating Paradise: A Comprehensive Guide To Sandals Resort Locations
- A Coastal Tapestry: Exploring Washington State’s Diverse Shoreline
- Navigating The Beauty Of Utah: A Comprehensive Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply