Navigating The Thermal Tapestry Of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide To Temperature Patterns
Navigating the Thermal Tapestry of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Patterns
Related Articles: Navigating the Thermal Tapestry of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Patterns
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Thermal Tapestry of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Patterns. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Thermal Tapestry of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Patterns

Europe, a continent of diverse landscapes and cultures, also boasts a wide spectrum of climates, with temperature variations playing a crucial role in shaping its environment, ecosystems, and human activities. Understanding the distribution of temperatures across Europe is essential for a multitude of applications, from agriculture and tourism to infrastructure planning and climate change mitigation. This article delves into the complexities of European temperature patterns, exploring the factors that influence them, the geographical distribution of heat and cold, and the implications of these variations for society and the environment.
The Building Blocks of European Temperature Patterns:
Several key factors contribute to the intricate tapestry of European temperatures:
- Latitude: As a continent stretching from the Arctic Circle to the Mediterranean Sea, Europe experiences a wide range of solar radiation due to its latitudinal extent. Northern regions receive less solar energy, resulting in colder temperatures, while southern regions bask in more sunlight, leading to warmer climates.
- Ocean Currents: The North Atlantic Current, a warm current originating in the Gulf of Mexico, significantly influences Western Europe’s climate, moderating its temperatures and bringing milder winters compared to regions at similar latitudes. Conversely, the cold Labrador Current, originating in the Arctic, cools the eastern coast of North America, influencing the temperature patterns of the North Atlantic.
- Altitude: Mountains act as barriers to air movement, creating distinct microclimates. Higher altitudes experience significantly lower temperatures due to the thinner atmosphere and reduced air pressure, resulting in cooler conditions even in regions with generally warm climates.
- Continentality: Inland areas, far from the moderating influence of oceans, experience greater temperature fluctuations between seasons. Summers are hotter, and winters are colder in continental regions compared to coastal areas.
- Orographic Effects: Mountains force air to rise, leading to cooling and condensation, often resulting in precipitation. The resulting rain shadow effect, where the leeward side of mountains receives less rainfall, can also influence temperature patterns, creating drier and warmer conditions.
A Geographical Overview of European Temperatures:
Europe’s temperature patterns can be broadly divided into several distinct regions:
- Northern Europe: Dominated by a subarctic climate, characterized by long, cold winters and short, cool summers. Average temperatures in the region range from -5°C to 15°C, with significant variations depending on location and altitude.
- Western Europe: Benefiting from the North Atlantic Current, Western Europe enjoys a temperate climate with mild winters and warm summers. Average temperatures range from 5°C to 20°C, with the coastal areas generally experiencing milder conditions than inland regions.
- Central Europe: A transitional zone between the temperate and continental climates, Central Europe experiences four distinct seasons. Winters are cold, with average temperatures around 0°C, while summers are warm, with average temperatures around 20°C.
- Eastern Europe: Marked by a continental climate, Eastern Europe experiences extreme temperature variations between seasons. Summers are hot, with average temperatures exceeding 25°C, while winters are cold, with average temperatures often dropping below -5°C.
- Southern Europe: Home to a Mediterranean climate, Southern Europe enjoys mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. Average temperatures range from 10°C to 25°C, with the southernmost regions experiencing the highest temperatures.
The Importance of Understanding European Temperatures:
The significance of comprehending European temperature patterns is multifaceted:
- Agriculture: Temperature influences crop yields and agricultural practices. Understanding temperature patterns helps farmers optimize planting schedules, select suitable crops, and implement appropriate irrigation strategies.
- Tourism: Temperature is a critical factor in tourist destinations, influencing travel seasons and the popularity of various activities. Understanding temperature patterns helps tourists plan their trips effectively and select destinations based on their desired climate.
- Infrastructure Planning: Temperature variations can affect infrastructure design and construction. For example, understanding temperature extremes is crucial for designing buildings, roads, and bridges to withstand harsh conditions.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Analyzing temperature trends and patterns provides valuable insights into the impacts of climate change and helps inform strategies for adaptation and mitigation.
FAQs about European Temperatures:
Q: What are the hottest and coldest places in Europe?
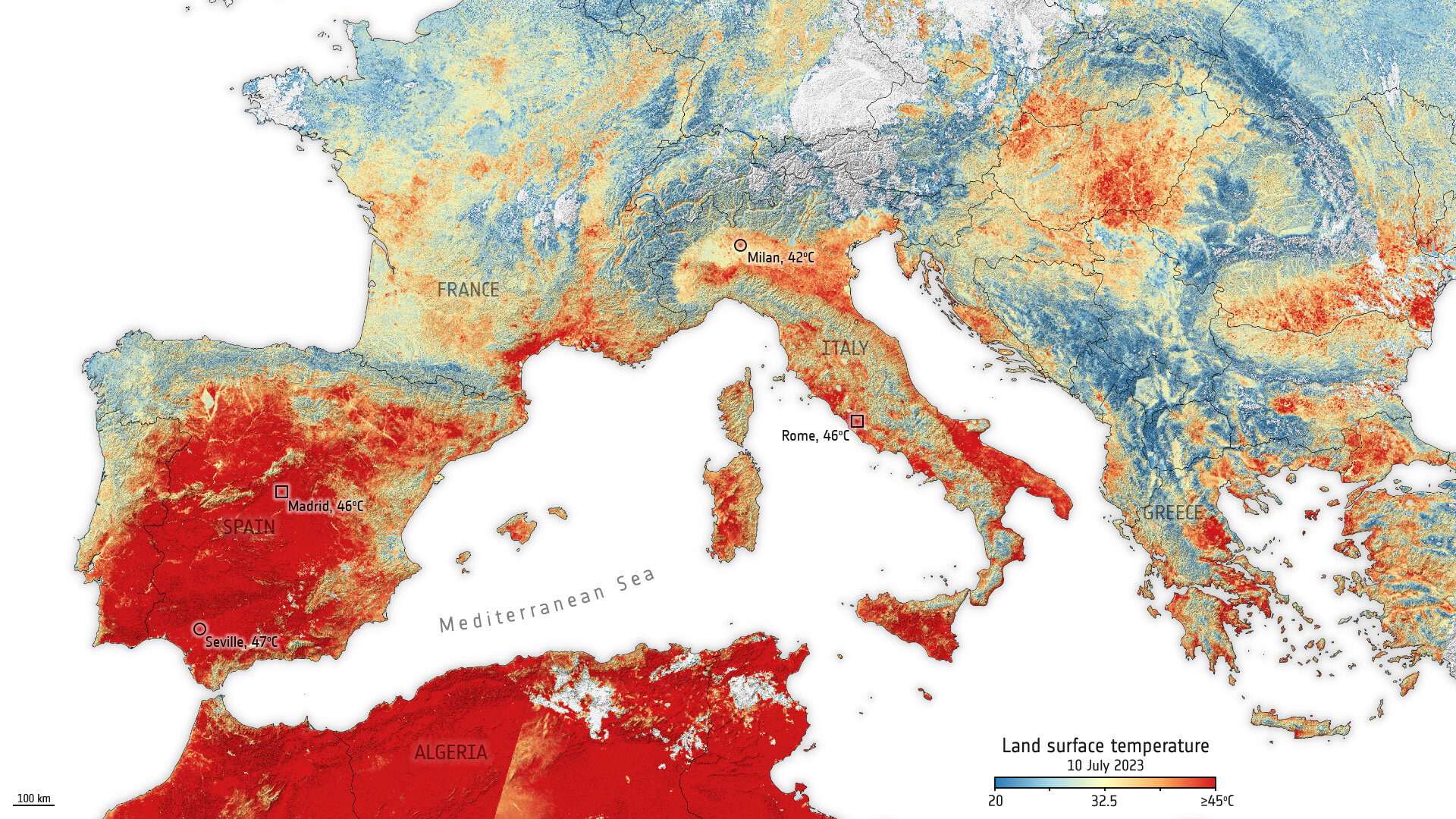
A: The hottest place in Europe is typically considered to be the southeastern region of Spain, particularly the Guadalquivir Valley, where temperatures can reach over 40°C in the summer months. The coldest place in Europe is located in the Ural Mountains, specifically the town of Oymyakon in Siberia, where temperatures can plummet to -67°C in winter.
Q: How does climate change affect European temperatures?
A: Climate change is causing an increase in average temperatures across Europe. This warming trend is particularly pronounced in the northern regions, leading to changes in plant and animal life, melting glaciers, and rising sea levels.
Q: How can I find detailed information about European temperatures?
A: Numerous sources provide detailed information about European temperatures, including:
- National Meteorological Services: Each country in Europe has a national meteorological service that provides detailed weather data, including temperature records.
- European Climate Change Portal: This portal offers a wealth of information about climate change in Europe, including temperature trends and projections.
- Scientific Journals: Scientific journals publish research papers on climate change and temperature patterns in Europe.
Tips for Navigating European Temperatures:
- Check the weather forecast: Before traveling to Europe, check the weather forecast for the specific region you are visiting.
- Pack appropriate clothing: Pack for a range of temperatures, as weather conditions can vary significantly throughout the day and across different regions.
- Be aware of heat waves: During summer months, be mindful of heat waves and take precautions to stay hydrated and avoid strenuous activities during the hottest hours.
- Be prepared for cold weather: Pack warm clothing, especially if you are traveling to northern or mountainous regions during the winter months.
Conclusion:
The intricate tapestry of European temperatures, shaped by a combination of geographical factors, plays a pivotal role in shaping the continent’s environment, ecosystems, and human activities. Understanding these patterns is essential for a multitude of applications, from agriculture and tourism to infrastructure planning and climate change mitigation. By delving into the nuances of European temperatures, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of our planet’s climate and the interconnectedness of its various components.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Thermal Tapestry of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Patterns. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Future: A Deep Dive Into SAP’s Roadmap
- Vanguard: A Comprehensive Exploration Of The Map
- Navigating The African Continent: Understanding Longitude And Latitude
- Unpacking The Geography Of East Europe And Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
- Interstate 5: A Vital Artery Connecting The West Coast
- Navigating Paradise: A Comprehensive Guide To Sandals Resort Locations
- A Coastal Tapestry: Exploring Washington State’s Diverse Shoreline
- Navigating The Beauty Of Utah: A Comprehensive Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply