Navigating The Radio Waves: A Comprehensive Guide To HF Propagation Maps
Navigating the Radio Waves: A Comprehensive Guide to HF Propagation Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Radio Waves: A Comprehensive Guide to HF Propagation Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Radio Waves: A Comprehensive Guide to HF Propagation Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Radio Waves: A Comprehensive Guide to HF Propagation Maps

The realm of high-frequency (HF) radio communication, often referred to as shortwave, is governed by complex interactions between the Earth’s atmosphere and the sun’s energy. Understanding these interactions is crucial for ensuring reliable HF communication, particularly for long-distance transmissions. Here, we delve into the critical role of HF propagation maps, tools that visualize the intricate pathways radio waves take, enabling informed decision-making for successful communication.
Decoding the Path of Radio Waves:
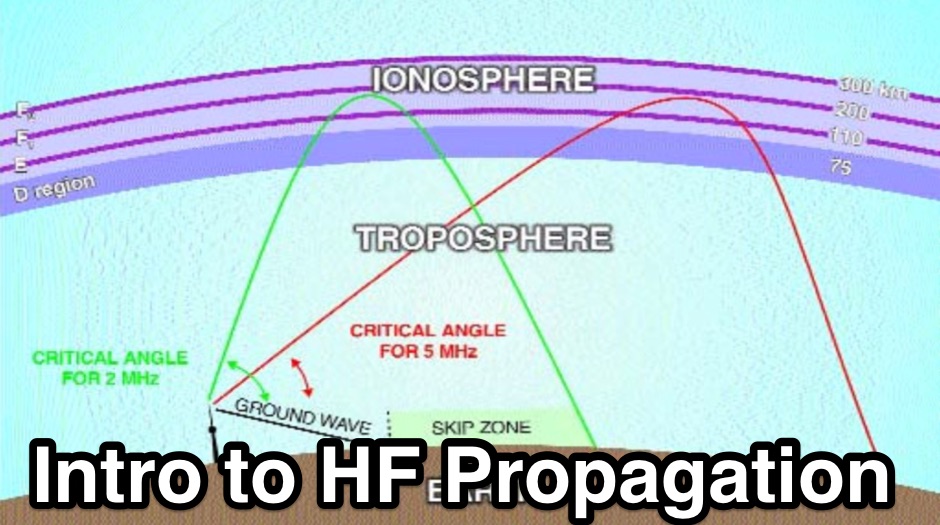
HF radio waves, unlike their lower-frequency counterparts, possess the unique ability to reflect off the ionosphere, a layer of charged particles in the Earth’s upper atmosphere. This reflection allows signals to travel beyond the horizon, enabling communication across vast distances. However, the ionosphere’s composition and density fluctuate constantly, influenced by solar activity and other factors, creating dynamic and unpredictable propagation conditions.
HF Propagation Maps: A Visual Guide to Radio Wave Behavior:
HF propagation maps, often referred to as "shortwave maps," are graphical representations that depict the predicted propagation conditions for various frequencies at a specific time. These maps utilize complex algorithms and real-time data from monitoring stations to visualize the following:
- Maximum Usable Frequency (MUF): The highest frequency that can be reflected by the ionosphere at a given time and location.
- Lowest Usable Frequency (LUF): The lowest frequency that can reliably propagate between two points.
- Great Circle Path (GCP): The shortest distance between two points on the Earth’s surface, representing the optimal path for radio wave propagation.
- Skip Zone: An area where radio waves cannot be received due to their inability to reach the ionosphere at a suitable angle for reflection.
- Signal Strength: The predicted strength of the received signal, often represented by color gradients or numerical values.
Unveiling the Importance of HF Propagation Maps:
HF propagation maps are indispensable tools for various applications, including:
- Amateur Radio Operators: Understanding the optimal frequencies and times for long-distance communication, maximizing signal strength and reach.
- Broadcasting Stations: Selecting the most effective frequencies for transmitting signals to remote audiences, optimizing coverage and audience engagement.
- Military and Emergency Services: Ensuring reliable communication during natural disasters or emergencies, where traditional infrastructure may be compromised.
- Scientific Research: Studying the ionosphere’s behavior and its impact on radio wave propagation, contributing to a deeper understanding of the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Navigation and Positioning Systems: Optimizing the performance of radio-based navigation systems, ensuring accurate positioning and reliable data transmission.
Navigating the Landscape of HF Propagation Maps:
Numerous resources provide access to HF propagation maps, each with its own unique features and functionalities. Some prominent examples include:
- VOACAP (Voice of America CAPability Program): A comprehensive and widely-used tool developed by the United States Department of Defense, offering detailed predictions for various frequencies and locations.
- HamCAP (Ham Radio CAPability Program): A specialized version of VOACAP tailored for amateur radio operators, providing user-friendly interface and specific parameters for ham radio applications.
- PROPNET: A collaborative project that gathers data from various sources to provide real-time propagation information, offering a global perspective on HF conditions.
- Online Mapping Services: Numerous websites offer interactive maps that visualize current propagation conditions, allowing users to explore specific locations and frequencies.
Frequently Asked Questions about HF Propagation Maps:
1. What factors influence HF propagation?
HF propagation is influenced by a multitude of factors, including solar activity, time of day, season, geographic location, and atmospheric conditions. Solar flares, sunspots, and geomagnetic storms significantly impact the ionosphere’s density and composition, altering radio wave propagation patterns.
2. How accurate are HF propagation maps?
HF propagation maps rely on complex algorithms and real-time data, providing reasonably accurate predictions. However, the ionosphere’s dynamic nature can introduce uncertainties, and actual propagation conditions may deviate from predictions.
3. How often should I consult HF propagation maps?
It is recommended to consult HF propagation maps regularly, especially before initiating long-distance communication. Changes in solar activity and atmospheric conditions can occur rapidly, impacting propagation patterns and requiring adjustments to communication frequencies.
4. Are there any limitations to HF propagation maps?
While HF propagation maps provide valuable insights, they are not perfect predictors. Local weather conditions, terrain features, and other factors can influence signal strength and propagation paths, potentially affecting communication quality.
5. How can I improve my understanding of HF propagation?
Engaging with the amateur radio community, participating in online forums, and reading specialized publications can enhance your understanding of HF propagation. Numerous resources offer comprehensive explanations and practical tips for utilizing HF propagation maps effectively.
Tips for Effective Use of HF Propagation Maps:
- Understand the terminology: Familiarize yourself with key terms like MUF, LUF, GCP, and skip zone to interpret propagation maps accurately.
- Consider your specific needs: Determine the frequency range and geographic locations relevant to your communication requirements.
- Compare multiple sources: Refer to different propagation maps and resources to gain a comprehensive understanding of current conditions.
- Adjust your frequencies: Experiment with different frequencies based on the predicted propagation conditions to optimize signal strength and reach.
- Monitor real-time conditions: Utilize online resources and monitoring tools to track changes in propagation patterns and adjust communication strategies accordingly.
Conclusion:
HF propagation maps are essential tools for navigating the complex world of high-frequency radio communication. By visualizing the intricate pathways radio waves take, these maps enable informed decision-making, ensuring reliable communication across vast distances. Understanding the principles behind HF propagation and utilizing available resources effectively empowers users to optimize communication performance and unlock the full potential of this fascinating communication medium.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Radio Waves: A Comprehensive Guide to HF Propagation Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Future: A Deep Dive Into SAP’s Roadmap
- Vanguard: A Comprehensive Exploration Of The Map
- Navigating The African Continent: Understanding Longitude And Latitude
- Unpacking The Geography Of East Europe And Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
- Interstate 5: A Vital Artery Connecting The West Coast
- Navigating Paradise: A Comprehensive Guide To Sandals Resort Locations
- A Coastal Tapestry: Exploring Washington State’s Diverse Shoreline
- Navigating The Beauty Of Utah: A Comprehensive Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply