Navigating The Archipelago Of Africa: A Comprehensive Guide To The Continent’s Islands
Navigating the Archipelago of Africa: A Comprehensive Guide to the Continent’s Islands
Related Articles: Navigating the Archipelago of Africa: A Comprehensive Guide to the Continent’s Islands
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Archipelago of Africa: A Comprehensive Guide to the Continent’s Islands. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Archipelago of Africa: A Comprehensive Guide to the Continent’s Islands
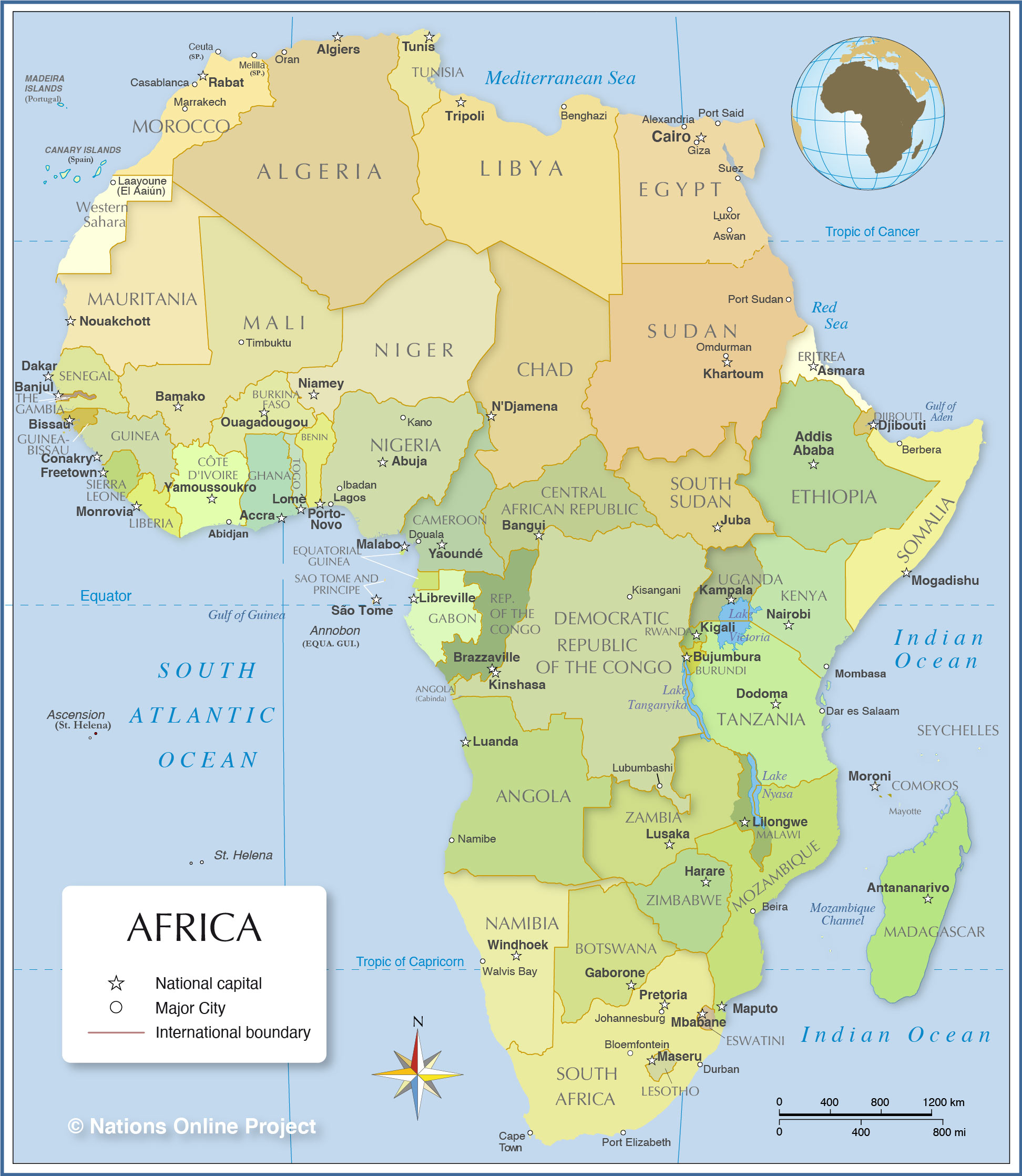
Africa, a continent renowned for its vast savannas, towering mountains, and diverse wildlife, also boasts a captivating archipelago of islands scattered across its surrounding waters. These islands, varying in size, geological formation, and cultural heritage, offer a unique perspective on the continent’s rich history, biodiversity, and potential. Understanding the geography and significance of these islands is crucial for comprehending the complexities of Africa’s landscape, its interactions with the surrounding world, and its potential for future development.
A Tapestry of Islands:
Africa’s islands can be broadly categorized into two main groups: continental islands and oceanic islands. Continental islands, often referred to as "offshore islands," are geologically connected to the mainland, having once formed part of the African landmass. These islands, such as Madagascar, Zanzibar, and the Comoros, share geological and biological similarities with the mainland, showcasing the continent’s diverse ecosystems.
Oceanic islands, on the other hand, emerged from volcanic activity or coral reef formations, entirely detached from the African mainland. These islands, including the Seychelles, São Tomé and Príncipe, and the Canary Islands, possess distinct geological and biological characteristics, showcasing the unique processes of island evolution.
Exploring the Archipelago:
Madagascar: The largest island off the African coast, Madagascar is a biodiversity hotspot, home to a staggering array of endemic species found nowhere else on Earth. Its unique flora and fauna, including the iconic lemurs, reflect millions of years of isolation and evolution. Madagascar’s diverse landscapes, ranging from lush rainforests to arid deserts, offer a captivating glimpse into the continent’s ecological richness.
Zanzibar: This Tanzanian archipelago, renowned for its spice plantations and pristine beaches, is a cultural crossroads where African, Arab, and Indian influences blend seamlessly. Zanzibar’s history is intertwined with the spice trade, which brought prosperity and cultural exchange to the islands. Today, Zanzibar is a popular tourist destination, attracting visitors from across the globe.
Comoros: This volcanic archipelago, located between Madagascar and Mozambique, offers breathtaking views of active volcanoes and lush landscapes. The islands are known for their diverse flora and fauna, including endemic birds and reptiles. Comoros’s unique culture, influenced by Arab, French, and African traditions, adds to its captivating appeal.
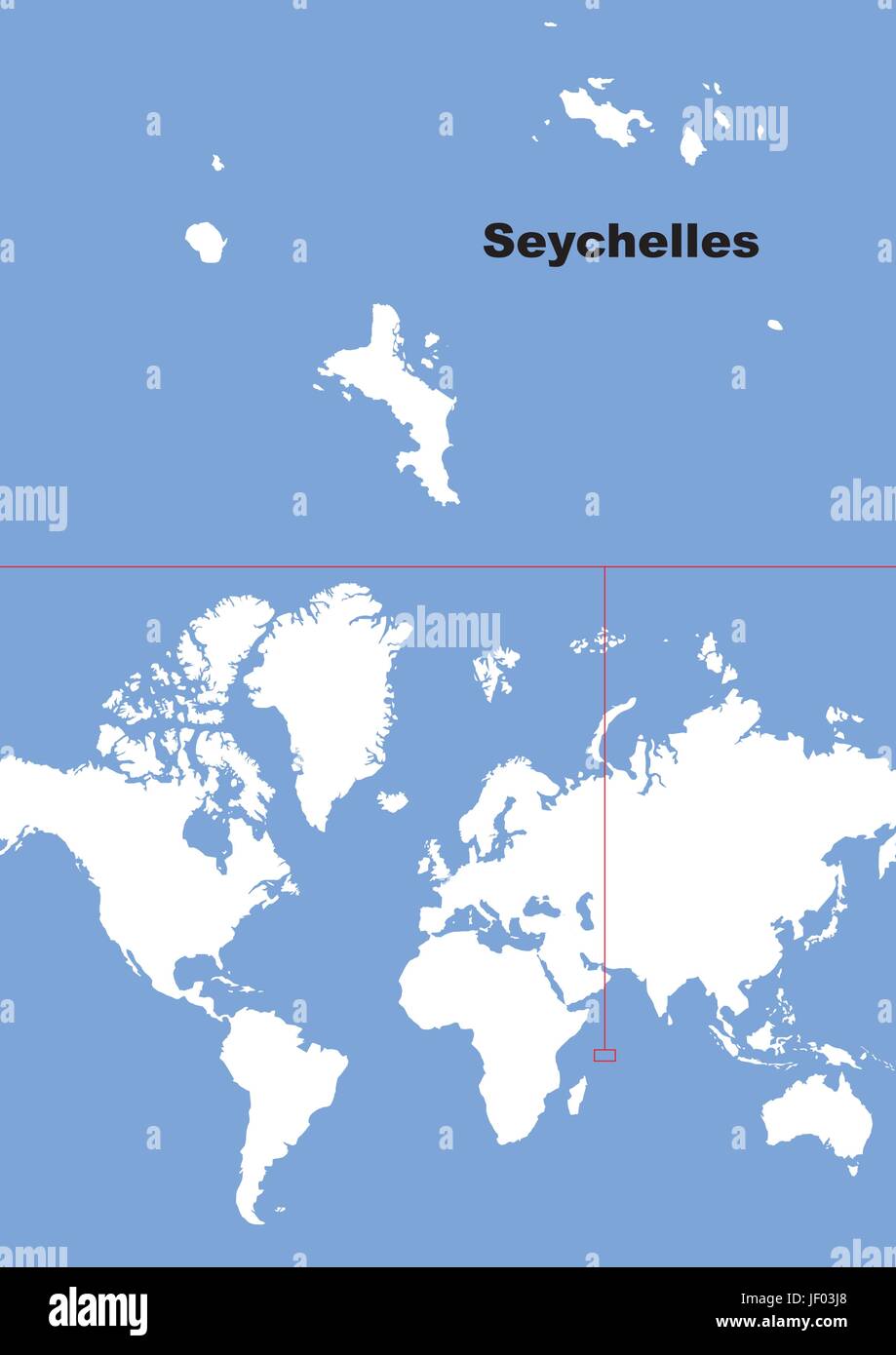
Seychelles: This archipelago, situated in the Indian Ocean, is renowned for its pristine beaches, granite rock formations, and diverse marine life. The Seychelles’ unique flora and fauna, including the iconic giant tortoises, reflect its long isolation and unique evolutionary journey.
São Tomé and Príncipe: These volcanic islands, nestled in the Gulf of Guinea, offer a glimpse into the rich history of Portuguese colonization. The islands’ diverse ecosystems, ranging from rainforests to volcanic peaks, are home to a variety of endemic species.
Canary Islands: This Spanish archipelago, located off the coast of Northwest Africa, boasts diverse landscapes ranging from volcanic craters to lush forests. The Canary Islands are renowned for their unique flora and fauna, including the iconic dragon tree.
Importance and Benefits:
Africa’s islands play a crucial role in the continent’s economy, environment, and culture. They contribute to:
- Economic Development: Many islands, particularly those with pristine beaches and diverse ecosystems, are important tourist destinations, generating revenue and creating employment opportunities.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Islands are often home to unique species found nowhere else on Earth, making them crucial for biodiversity conservation.
- Cultural Heritage: Islands often possess distinct cultural identities, shaped by their history, isolation, and interaction with other cultures.
- Resource Management: Islands are vital for fisheries and other marine resources, playing a crucial role in the livelihoods of coastal communities.
- Scientific Research: Islands offer valuable opportunities for scientific research, particularly in areas like evolution, ecology, and climate change.
FAQs:
Q: What are the largest islands off the African coast?
A: The largest islands off the African coast are Madagascar, São Tomé, and Príncipe.
Q: What are the most popular tourist destinations among African islands?
A: Popular tourist destinations include Zanzibar, Seychelles, and the Canary Islands.
Q: What makes African islands unique in terms of biodiversity?
A: Many African islands have evolved unique flora and fauna due to their long isolation from the mainland. This has led to a high percentage of endemic species, found nowhere else on Earth.
Q: What are the major threats to African islands?
A: Threats to African islands include habitat loss, invasive species, climate change, and unsustainable tourism practices.
Tips:
- Research and Plan: Before visiting an African island, research its unique features, culture, and potential threats.
- Respect Local Cultures: Be respectful of local customs and traditions, and avoid actions that might be considered offensive.
- Support Sustainable Tourism: Choose eco-friendly accommodations and activities that minimize environmental impact.
- Protect Biodiversity: Be mindful of your actions and avoid disturbing wildlife or introducing invasive species.
- Engage with Local Communities: Interact with local communities and learn about their culture and traditions.
Conclusion:
Africa’s islands are more than just dots on a map. They represent a rich tapestry of ecosystems, cultures, and histories, offering a unique perspective on the continent’s diverse landscape and potential. Understanding the importance and challenges facing these islands is crucial for ensuring their future sustainability and the preservation of their unique treasures for generations to come. By embracing responsible tourism, supporting conservation efforts, and respecting local cultures, we can contribute to the well-being of these islands and the communities that call them home.
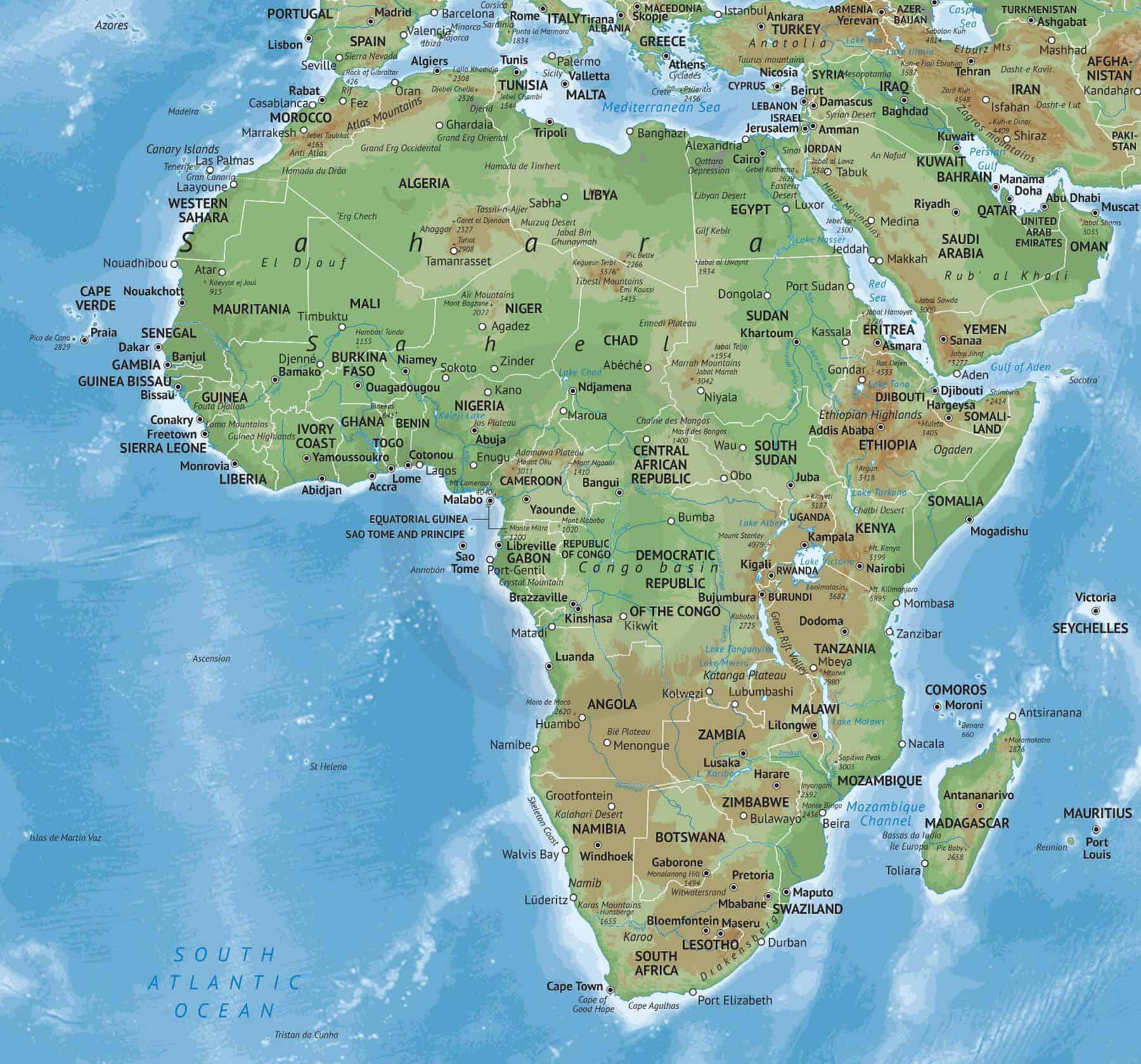

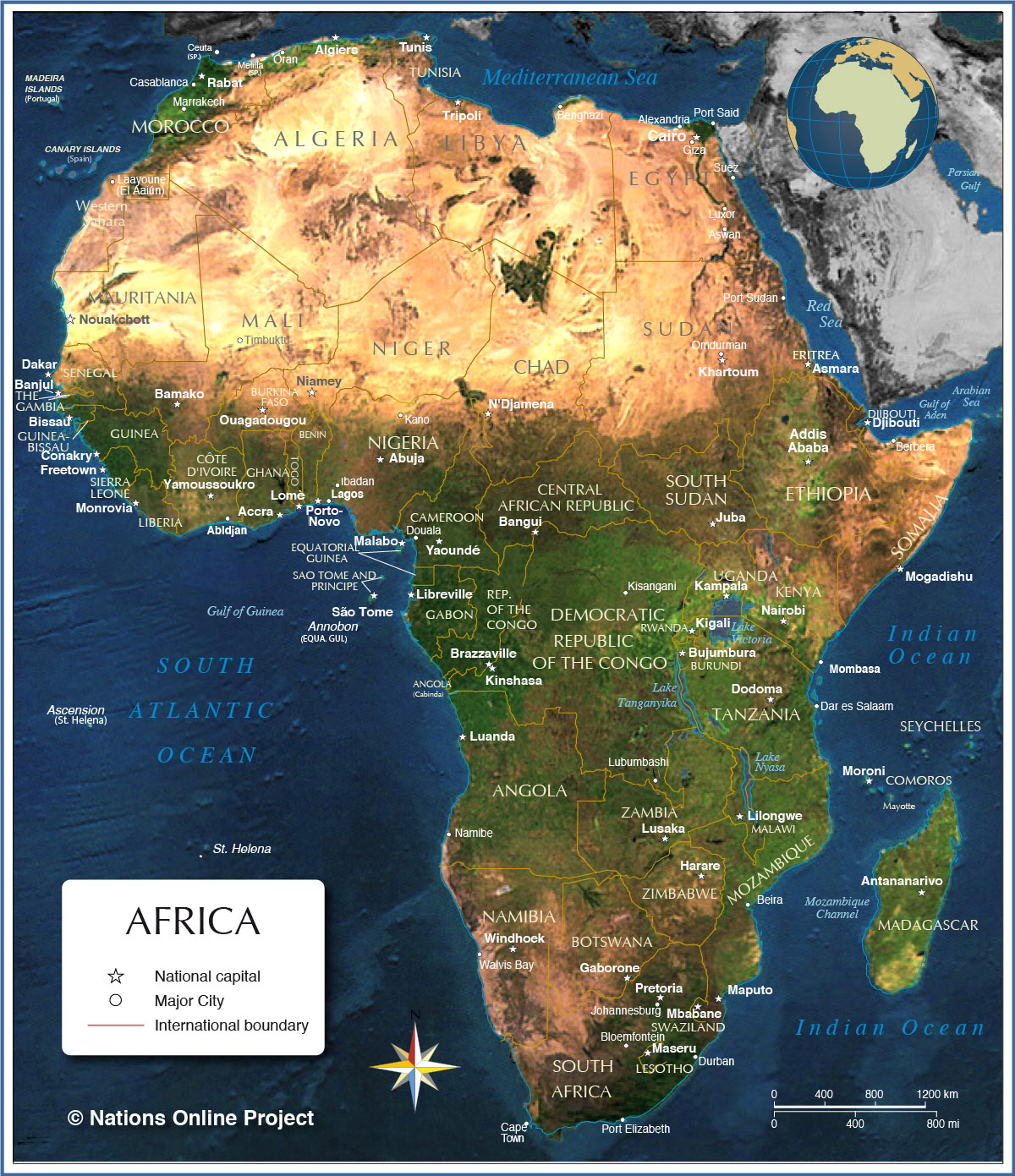


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Archipelago of Africa: A Comprehensive Guide to the Continent’s Islands. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Future: A Deep Dive Into SAP’s Roadmap
- Vanguard: A Comprehensive Exploration Of The Map
- Navigating The African Continent: Understanding Longitude And Latitude
- Unpacking The Geography Of East Europe And Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
- Interstate 5: A Vital Artery Connecting The West Coast
- Navigating Paradise: A Comprehensive Guide To Sandals Resort Locations
- A Coastal Tapestry: Exploring Washington State’s Diverse Shoreline
- Navigating The Beauty Of Utah: A Comprehensive Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply