Navigating The African Continent: Understanding Longitude And Latitude
Navigating the African Continent: Understanding Longitude and Latitude
Related Articles: Navigating the African Continent: Understanding Longitude and Latitude
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the African Continent: Understanding Longitude and Latitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the African Continent: Understanding Longitude and Latitude
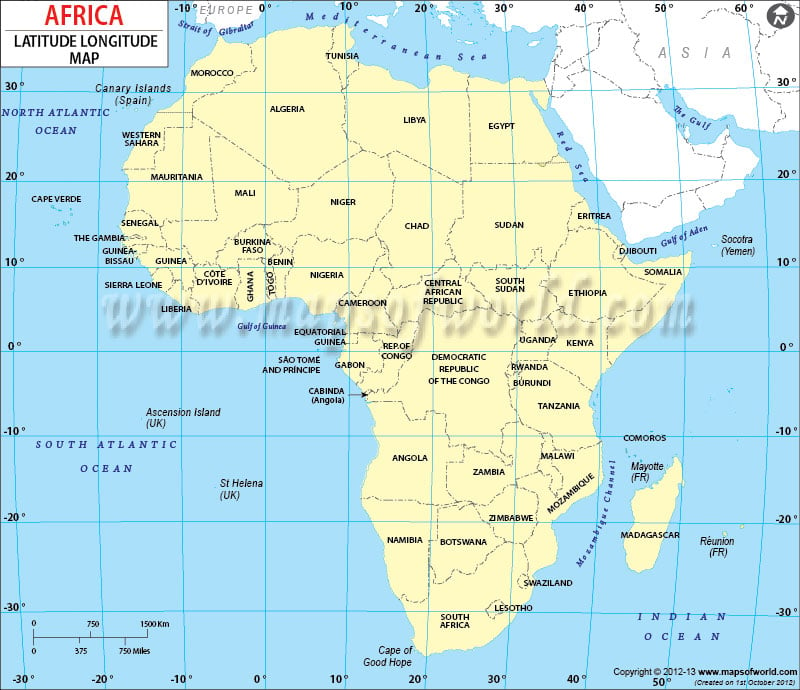
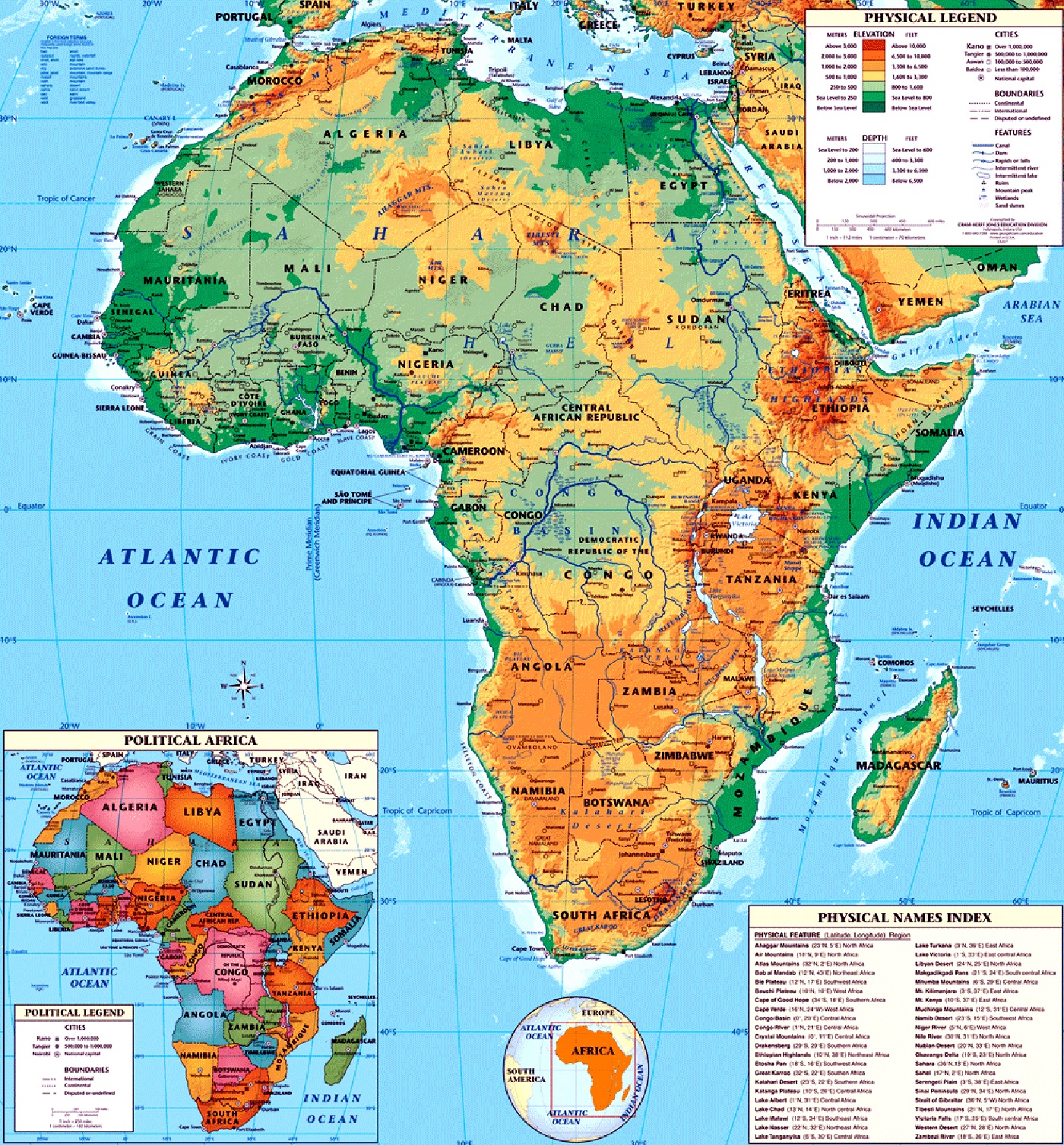
Africa, the second-largest continent, boasts a diverse tapestry of landscapes, cultures, and ecosystems. Navigating this vast expanse requires a robust framework for understanding its geographical coordinates. Longitude and latitude, the two fundamental components of the global grid system, provide the necessary framework for pinpointing any location on Earth, including the African continent.
The Grid System: Longitude and Latitude
Imagine the Earth as a perfect sphere. Longitude and latitude work together to create an invisible grid, slicing the globe into precise sections.
-
Longitude: Imagine vertical lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole, like slices in an orange. These lines represent longitude, measured in degrees east or west of the Prime Meridian, an imaginary line that runs through Greenwich, England. The Prime Meridian serves as the zero-degree line, with longitudes increasing to 180 degrees east and 180 degrees west.
-
Latitude: Now, imagine horizontal circles circling the Earth, parallel to the equator. These circles represent latitude, measured in degrees north or south of the equator, an imaginary line that divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. The equator is designated as 0 degrees latitude, with latitudes increasing to 90 degrees north at the North Pole and 90 degrees south at the South Pole.
Africa’s Position on the Global Grid
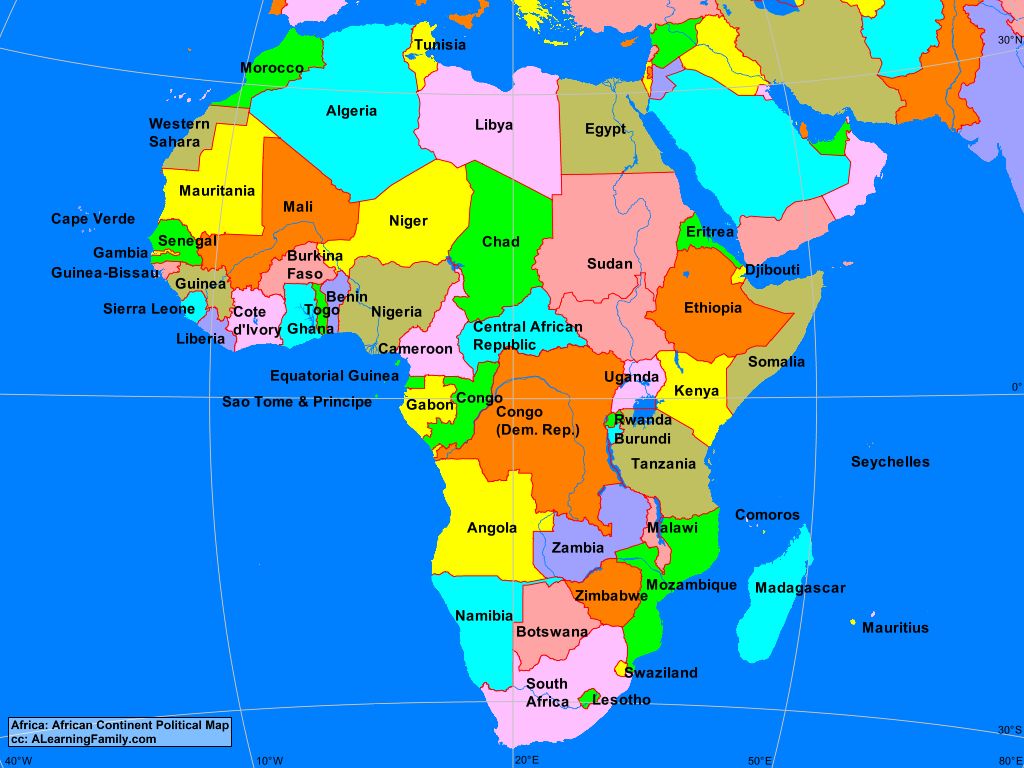
Africa lies predominantly in the Northern and Eastern hemispheres, spanning a significant range of longitudes and latitudes:
-
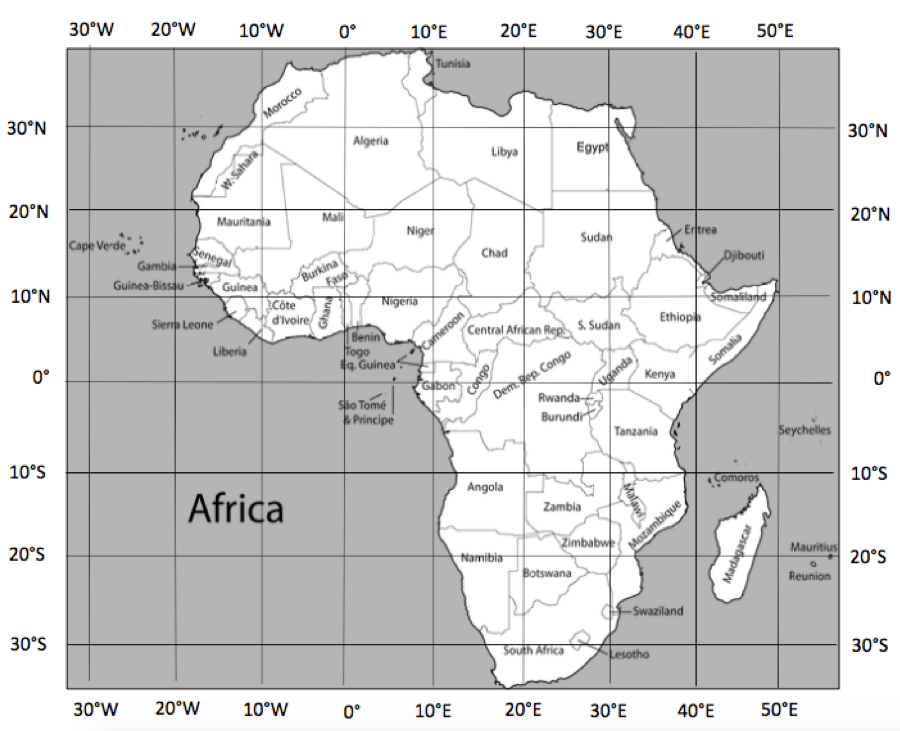
Longitude: Africa’s westernmost point is located at approximately 17° West, while its easternmost point reaches around 51° East. This vast longitudinal span encompasses a significant portion of the globe, covering diverse time zones and climates.
-
Latitude: Africa’s southernmost point, Cape Agulhas, sits at approximately 35° South, while its northernmost point, Ras ben Sakka in Tunisia, extends to 37° North. This latitudinal range places Africa within the tropical and subtropical regions, resulting in its characteristic warm climate and abundant biodiversity.
Benefits of Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Understanding the coordinates of Africa offers numerous benefits, including:
-
Precise Location Identification: Longitude and latitude provide the most accurate way to pinpoint any location on the continent. This is crucial for navigation, mapping, and geographical research.
-
Understanding Climate and Weather Patterns: Latitude plays a crucial role in determining climate zones. Africa’s location straddling the equator results in a predominantly tropical climate, with distinct variations across its vast landscape.
-
Mapping Biodiversity and Ecosystems: Latitude and longitude help map the distribution of various ecosystems, including rainforests, savannas, deserts, and coastal regions. This knowledge is vital for conservation efforts and understanding the continent’s rich biodiversity.
-
Facilitating Trade and Communication: Longitude and latitude are fundamental for global navigation, enabling efficient trade routes and communication networks across the African continent and beyond.
-
Supporting Scientific Research: These coordinates are indispensable for scientific research, particularly in fields like geology, climatology, and biodiversity studies.
FAQs about Longitude and Latitude in Africa
Q: What is the importance of the Prime Meridian for Africa?
A: The Prime Meridian, running through Greenwich, England, defines the zero-degree longitude. It is essential for determining the time zones across Africa.
Q: How do latitude and longitude influence Africa’s climate?
A: Latitude determines the amount of solar radiation received, impacting temperature and rainfall patterns. Africa’s location near the equator results in a predominantly tropical climate.
Q: What are the main climate zones in Africa based on latitude?
A: Africa’s climate zones are generally defined by latitude:
- Equatorial Zone: Near the equator, characterized by high temperatures and heavy rainfall.
- Tropical Zone: Located north and south of the equator, with distinct wet and dry seasons.
- Subtropical Zone: Further north and south, with drier climates and more pronounced seasonal variations.
Q: How do latitude and longitude influence Africa’s biodiversity?
A: Latitude influences the distribution of various ecosystems, resulting in different species adapted to specific environments.
Q: How do latitude and longitude aid in understanding Africa’s cultural diversity?
A: While not directly linked, latitude and longitude can indirectly influence cultural diversity. Geographic isolation, facilitated by physical barriers like mountains or deserts, can contribute to distinct cultural identities in specific regions.
Tips for Utilizing Latitude and Longitude in Africa
- Use online mapping tools: Interactive maps incorporating latitude and longitude allow for precise location identification and exploration.
- Consult atlases and geographical resources: Refer to detailed maps and geographical publications for accurate coordinates and regional information.
- Learn to interpret latitude and longitude values: Familiarize yourself with the system’s structure and how to read and interpret coordinates.
- Consider the impact of latitude on climate: When planning travel or conducting research, factor in the influence of latitude on weather and climate patterns.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricate relationship between longitude and latitude is essential for navigating and comprehending the vast and diverse continent of Africa. These coordinates provide a framework for precise location identification, climate analysis, biodiversity mapping, and various other applications. By harnessing the power of this grid system, we gain valuable insights into Africa’s unique geography, unlocking a deeper understanding of its complex and fascinating landscape.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the African Continent: Understanding Longitude and Latitude. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Future: A Deep Dive Into SAP’s Roadmap
- Vanguard: A Comprehensive Exploration Of The Map
- Navigating The African Continent: Understanding Longitude And Latitude
- Unpacking The Geography Of East Europe And Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
- Interstate 5: A Vital Artery Connecting The West Coast
- Navigating Paradise: A Comprehensive Guide To Sandals Resort Locations
- A Coastal Tapestry: Exploring Washington State’s Diverse Shoreline
- Navigating The Beauty Of Utah: A Comprehensive Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply