Mapping The Rising Tide: Understanding Flood Risk In A Warming World
Mapping the Rising Tide: Understanding Flood Risk in a Warming World
Related Articles: Mapping the Rising Tide: Understanding Flood Risk in a Warming World
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Rising Tide: Understanding Flood Risk in a Warming World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Rising Tide: Understanding Flood Risk in a Warming World
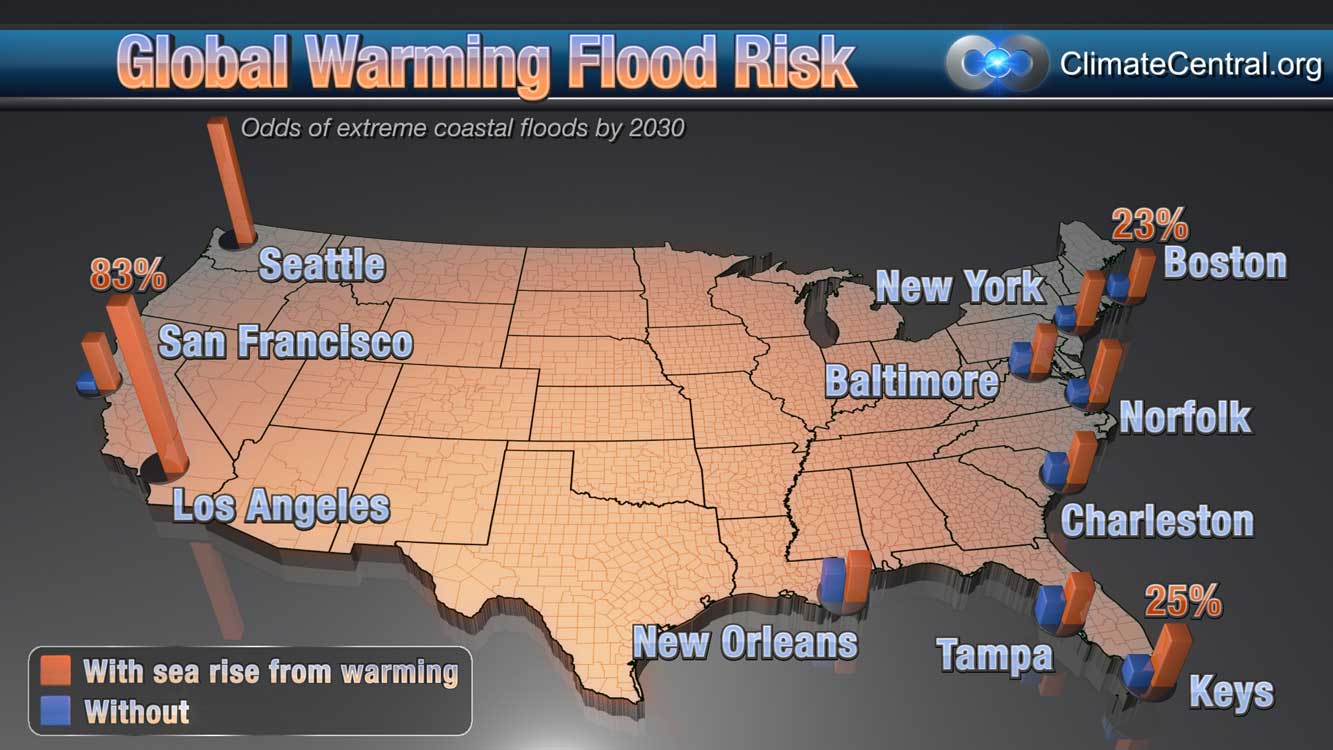
The Earth is warming, and with it, the oceans are rising. This seemingly slow and gradual process carries with it a profound and escalating threat: increased flooding. Coastal communities, riverine settlements, and even inland areas are facing a growing risk of inundation, driven by a combination of factors intricately linked to climate change. Understanding this complex interplay is crucial for mitigating the impacts and building resilience for the future.
The Intertwined Threads of Climate Change and Flooding
Global warming, fueled primarily by human activities, is altering the delicate balance of Earth’s climate system. The primary culprit is the release of greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide, which trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to a gradual increase in global temperatures. This warming trend has several direct and indirect impacts on flood risk:
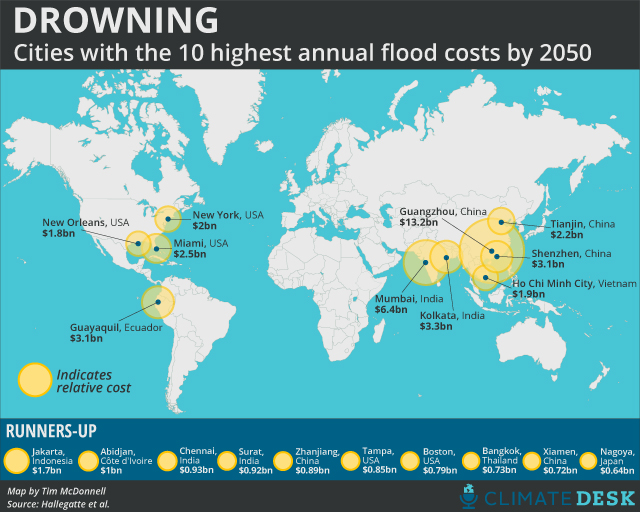
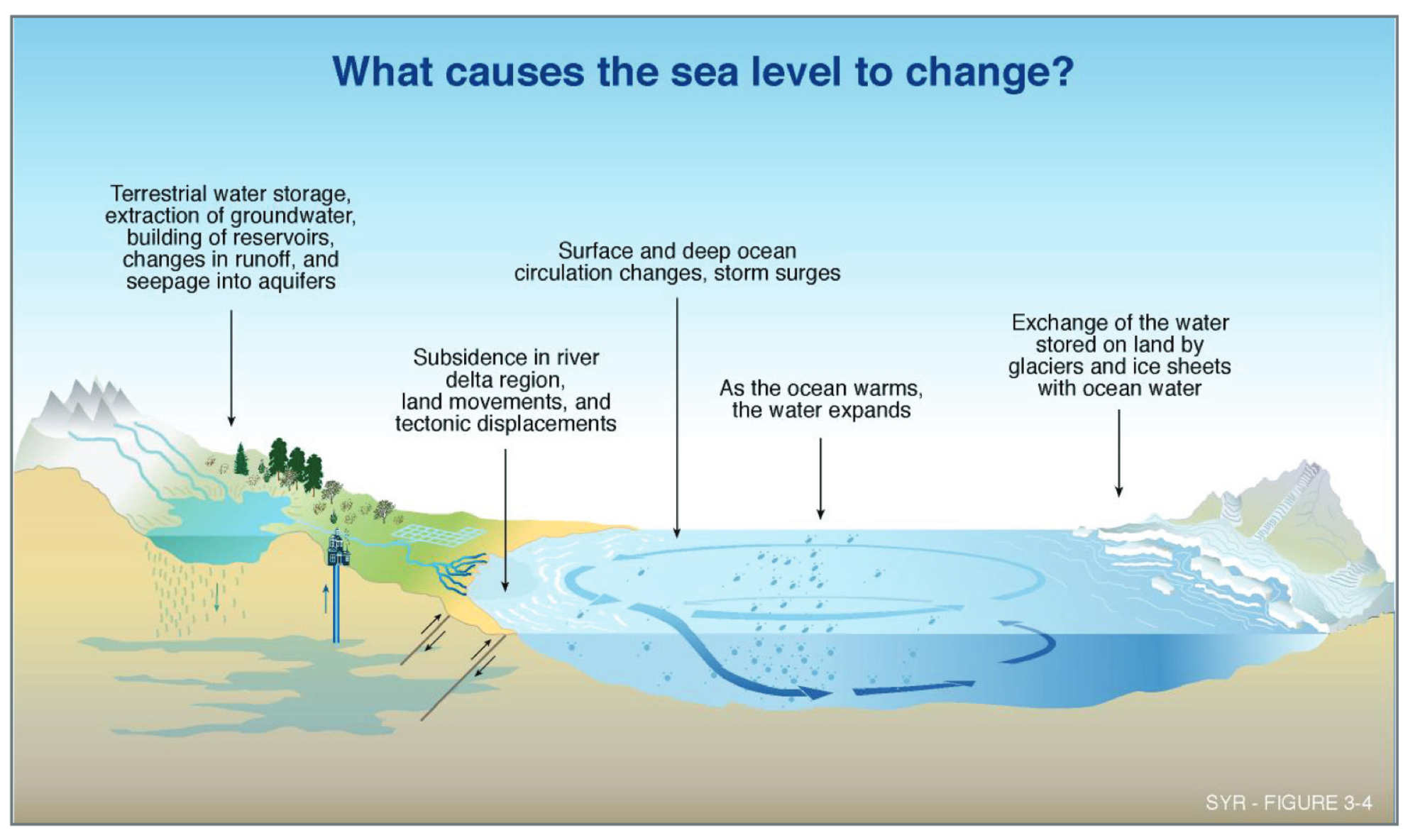
1. Sea Level Rise: As global temperatures rise, glaciers and ice sheets melt at an accelerated rate, adding vast amounts of water to the oceans. Thermal expansion, where water expands as it warms, further contributes to rising sea levels. This encroaching tide threatens coastal communities, pushing back shorelines and increasing the frequency and severity of coastal flooding.
2. Extreme Weather Events: A warming atmosphere holds more moisture, leading to an intensification of precipitation patterns. This translates into more frequent and intense rainfall events, causing riverine flooding. Storms, such as hurricanes and typhoons, are also becoming more powerful due to warmer ocean temperatures, leading to storm surges and coastal inundation.
3. Changes in Ocean Currents and Circulation: Global warming disrupts ocean currents and circulation patterns, impacting weather systems and contributing to changes in precipitation patterns. This can lead to shifts in flood risk zones, with some areas experiencing increased flooding while others may see a decrease.
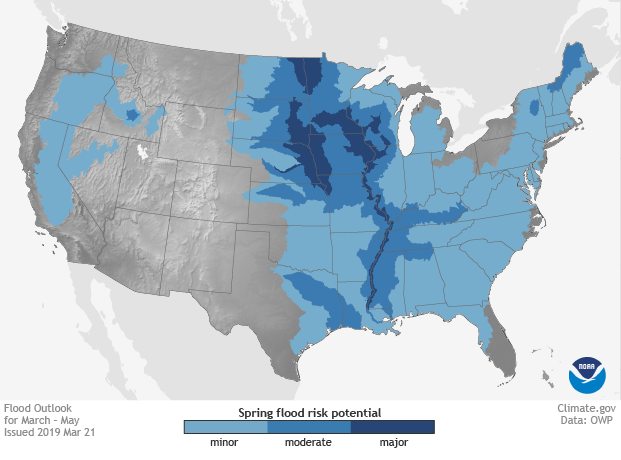
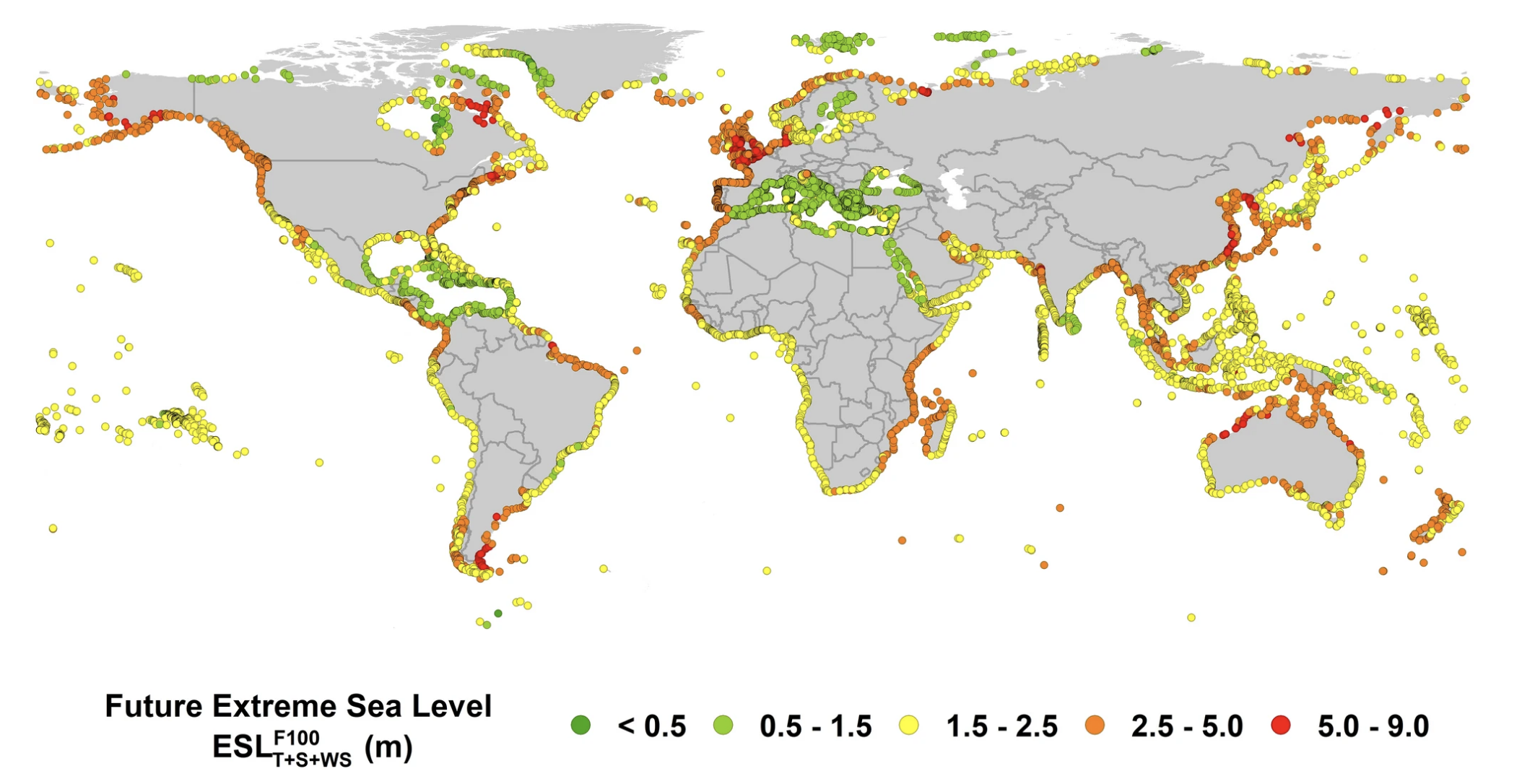
Flood Maps: A Vital Tool for Understanding and Planning
Flood maps are essential tools for visualizing and understanding the potential impacts of flooding. These maps, often created using sophisticated computer models and historical data, depict areas at risk of inundation under different scenarios, such as sea level rise projections or extreme rainfall events. They provide valuable information for:
- Risk Assessment: Flood maps enable communities to assess the extent and severity of potential flooding, helping them understand the vulnerability of infrastructure, homes, and businesses.
- Planning and Mitigation: By identifying flood-prone areas, communities can develop targeted strategies for mitigating flood risks, such as building seawalls, elevating structures, or implementing flood-resistant building codes.
- Emergency Response: Flood maps are crucial for emergency responders, enabling them to anticipate flood zones, plan evacuation routes, and allocate resources effectively during flood events.
- Insurance and Investment: Flood maps help insurance companies assess risk and determine premiums, while investors can use them to make informed decisions about development projects in flood-prone areas.
The Evolution of Flood Maps in a Changing Climate
As the climate continues to change, flood maps must evolve to reflect the dynamic nature of flood risk. This requires:
- Regular Updates: Flood maps need to be updated regularly, incorporating new data on sea level rise projections, changing precipitation patterns, and evolving coastal erosion trends.
- Scenario Planning: Flood maps should be developed for various scenarios, including different sea level rise projections and extreme weather events, to provide a comprehensive understanding of potential risks.
- Integration of Multiple Data Sources: Flood maps should incorporate data from various sources, including satellite imagery, ground-based sensors, and climate models, to provide a more accurate and holistic picture of flood risk.
- Community Engagement: Development of flood maps should involve communities, ensuring that their local knowledge and perspectives are integrated into the process, leading to more effective and relevant maps.
FAQs about Flood Maps and Climate Change
1. How accurate are flood maps?
Flood map accuracy depends on various factors, including the quality of data used, the sophistication of the models employed, and the specific scenario being modeled. While maps provide valuable insights, they should be considered as estimates, and their accuracy can vary depending on the location and the specific flood event.
2. How often are flood maps updated?
The frequency of updates varies depending on the jurisdiction and the rate of change in flood risk. Some maps are updated annually, while others may be updated less frequently. It’s important to consult the relevant authorities or organizations responsible for creating and maintaining flood maps for the most up-to-date information.
3. What are the limitations of flood maps?
Flood maps are valuable tools but have limitations. They may not account for all potential factors contributing to flooding, such as localized factors like drainage systems or land use changes. Additionally, they are based on historical data and may not accurately predict the impacts of extreme events that have not occurred previously.
4. How can I access flood maps for my area?
Flood maps are often available from government agencies, such as the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) in the United States or similar organizations in other countries. You can also consult local planning departments or insurance companies for access to flood maps in your area.
Tips for Using Flood Maps Effectively
- Understand the map’s limitations: Be aware that flood maps are estimates and may not capture all potential risks.
- Consult multiple sources: Compare maps from different sources to get a more comprehensive understanding of flood risk.
- Consider local factors: Factor in local conditions, such as drainage systems, land use changes, and infrastructure, which can influence flood risk.
- Engage with your community: Participate in local planning efforts and advocate for flood mitigation measures based on the information provided by flood maps.
Conclusion: A Call for Action and Adaptation
Flood maps are powerful tools for understanding and preparing for the growing threat of flooding in a changing climate. They provide vital information for risk assessment, planning, emergency response, and investment decisions. However, it is crucial to recognize that flood maps are just one piece of the puzzle. Addressing the root causes of climate change, implementing effective mitigation measures, and fostering community resilience are essential for navigating the challenges posed by a warming world and its rising tides.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Rising Tide: Understanding Flood Risk in a Warming World. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Future: A Deep Dive Into SAP’s Roadmap
- Vanguard: A Comprehensive Exploration Of The Map
- Navigating The African Continent: Understanding Longitude And Latitude
- Unpacking The Geography Of East Europe And Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
- Interstate 5: A Vital Artery Connecting The West Coast
- Navigating Paradise: A Comprehensive Guide To Sandals Resort Locations
- A Coastal Tapestry: Exploring Washington State’s Diverse Shoreline
- Navigating The Beauty Of Utah: A Comprehensive Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply