Deciphering The Weather: A Guide To Surface Forecast Maps
Deciphering the Weather: A Guide to Surface Forecast Maps
Related Articles: Deciphering the Weather: A Guide to Surface Forecast Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Weather: A Guide to Surface Forecast Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Weather: A Guide to Surface Forecast Maps

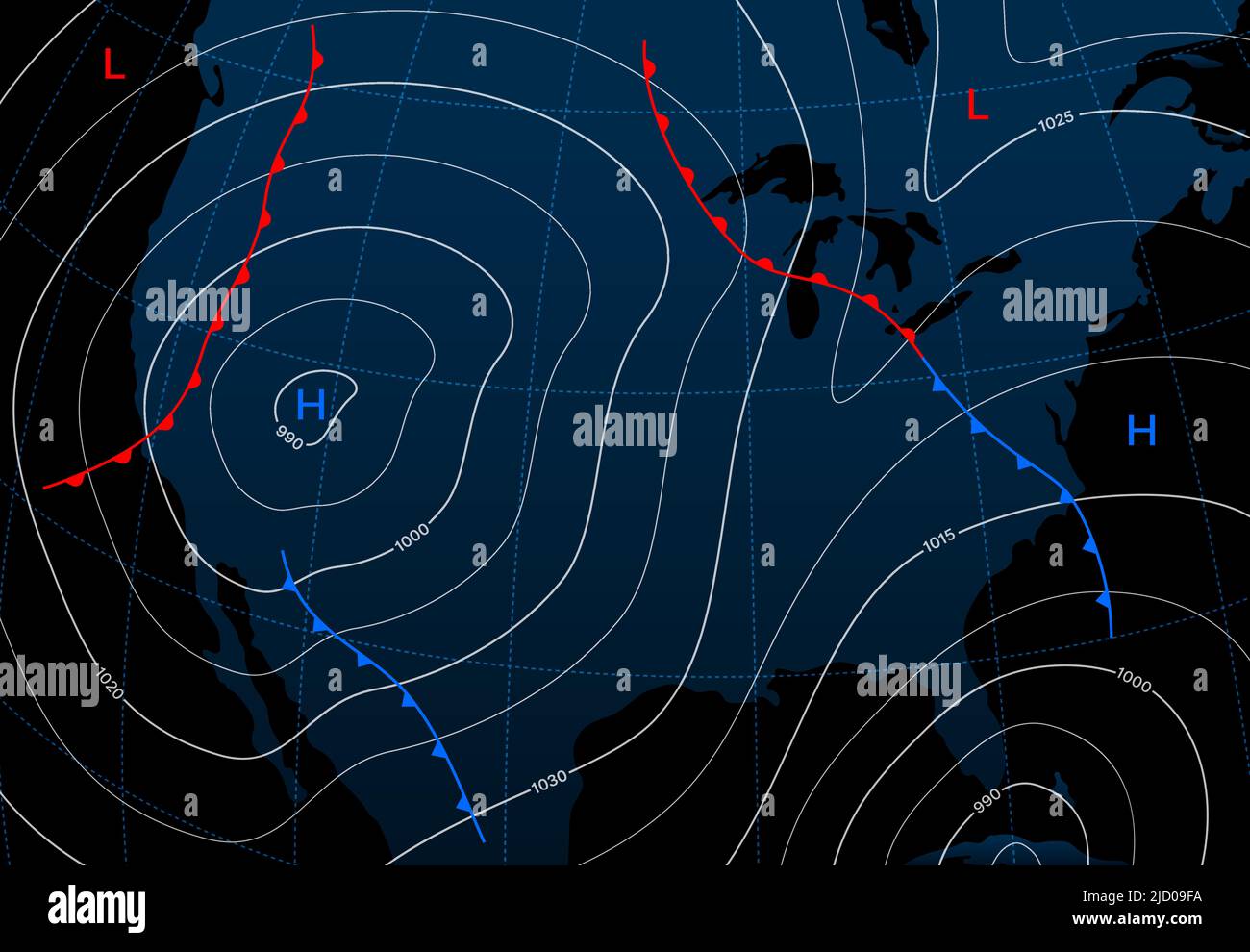
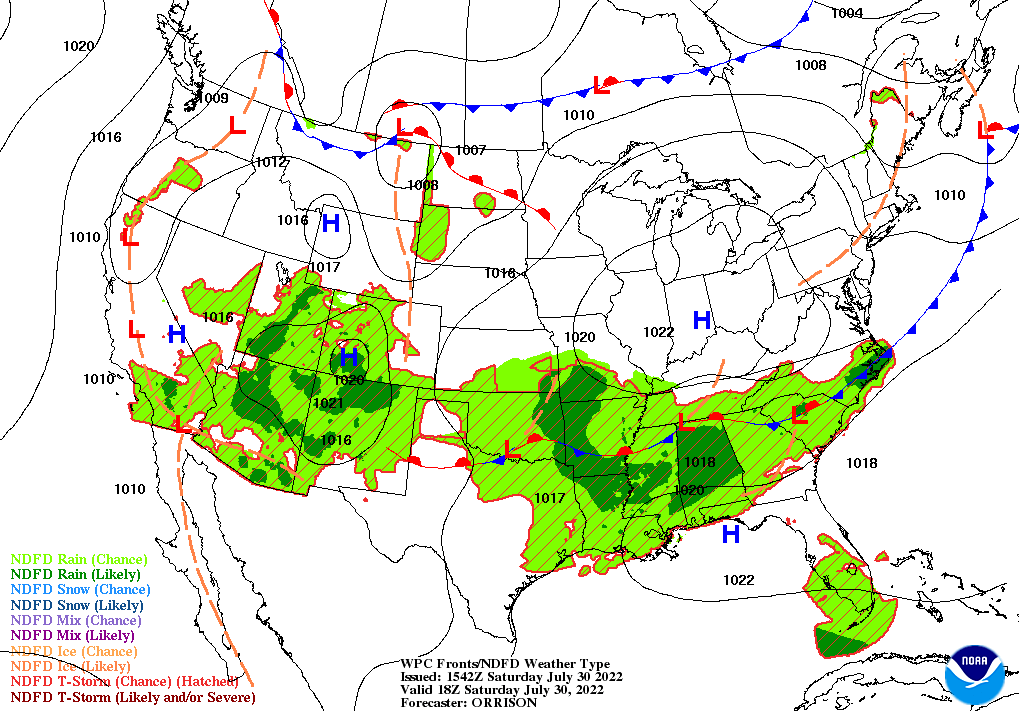
Surface forecast maps, often referred to as synoptic charts, are essential tools for meteorologists and anyone seeking to understand the current and predicted weather conditions. These maps provide a visual representation of atmospheric conditions at a specific point in time, offering a snapshot of the weather across a vast geographical area. By interpreting the symbols and data presented on these maps, individuals can gain valuable insights into various weather phenomena, including temperature, pressure, wind speed and direction, precipitation, and cloud cover.
Understanding the Elements of a Surface Forecast Map
A typical surface forecast map comprises several key elements:
- Isobars: These lines connect points of equal atmospheric pressure, revealing areas of high and low pressure. High-pressure areas are typically associated with clear skies and calm weather, while low-pressure areas often bring cloudiness, precipitation, and potentially stormy conditions.
- Isotherms: These lines connect points of equal temperature, illustrating the distribution of heat across the region. Warm air masses are often associated with high pressure, while cold air masses are linked to low pressure.
- Fronts: These boundaries separate air masses with different temperatures, humidity, and densities. Cold fronts, marked by blue lines with triangles, advance rapidly and bring sudden changes in temperature, often accompanied by thunderstorms and heavy precipitation. Warm fronts, marked by red lines with semicircles, move more slowly and bring gradual increases in temperature and humidity, often with widespread cloudiness and light precipitation.
- Wind Barbs: These symbols indicate wind speed and direction. The direction of the barb indicates the direction from which the wind is blowing, while the length of the barb represents the wind speed.
- Weather Symbols: Various symbols represent different weather conditions, such as precipitation (rain, snow, sleet, hail), cloud cover (clear, partly cloudy, overcast), and visibility (fog, mist, haze).
Decoding the Information on a Surface Forecast Map
By analyzing the interplay of these elements, forecasters can interpret the current weather patterns and predict future conditions. For instance, the convergence of isobars, particularly in low-pressure areas, often indicates areas of strong winds and potential for severe weather. The movement of fronts can be tracked to predict changes in temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns.
The Importance of Surface Forecast Maps
Surface forecast maps are crucial for a variety of applications:
- Aviation: Pilots use these maps to plan flight routes, assess wind conditions, and anticipate potential hazards like thunderstorms.
- Marine Navigation: Mariners rely on surface forecast maps to navigate safely, considering wind speed and direction, wave heights, and potential storms.
- Agriculture: Farmers utilize these maps to monitor temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns, influencing decisions regarding planting, irrigation, and harvesting.
- Emergency Management: Emergency responders use surface forecast maps to predict the potential impact of severe weather events, allowing for timely warnings and preparedness measures.
- Public Safety: Individuals can use surface forecast maps to stay informed about upcoming weather conditions, making informed decisions regarding outdoor activities, travel plans, and personal safety.
FAQs about Surface Forecast Maps
1. What is the difference between a surface forecast map and a weather radar map?
While both provide valuable information about weather conditions, surface forecast maps offer a broader overview of atmospheric conditions across a large area, using data from weather stations and other sources. Weather radar maps, on the other hand, provide a more localized and detailed picture of precipitation, revealing the intensity and movement of storms.
2. How often are surface forecast maps updated?
Surface forecast maps are typically updated every three to six hours, reflecting the dynamic nature of the atmosphere. However, the frequency of updates can vary depending on the specific forecasting agency and the level of detail required.
3. Can I access surface forecast maps online?
Yes, numerous online resources provide access to surface forecast maps, including government weather agencies like the National Weather Service (NWS) in the United States and the Met Office in the United Kingdom. Many private weather websites also offer interactive surface forecast maps with detailed information and user-friendly interfaces.
4. How can I learn to interpret surface forecast maps?
While interpreting surface forecast maps may seem daunting at first, several resources can help you develop your skills. Online tutorials, educational videos, and weather forecasting courses provide comprehensive guidance on understanding the symbols, data, and patterns presented on these maps.
Tips for Utilizing Surface Forecast Maps
- Consult multiple sources: Compare information from different sources, including government agencies, private weather websites, and local news outlets, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the weather situation.
- Consider the time frame: Pay attention to the time stamp of the map and understand that the forecast may change as weather conditions evolve.
- Look for trends: Analyze the movement of fronts, the evolution of pressure systems, and the changes in wind patterns to anticipate future weather developments.
- Use caution with forecasts: While surface forecast maps provide valuable insights, weather conditions can be unpredictable, and forecasts are not always perfectly accurate.
Conclusion
Surface forecast maps are indispensable tools for understanding and predicting weather conditions. By interpreting the data and symbols presented on these maps, individuals can gain valuable insights into atmospheric patterns, anticipate potential weather events, and make informed decisions regarding personal safety, travel plans, and various other activities. With the increasing availability of online resources and educational tools, understanding and utilizing surface forecast maps has become more accessible than ever before, empowering individuals to navigate the complexities of the weather with greater awareness and preparedness.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Weather: A Guide to Surface Forecast Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Future: A Deep Dive Into SAP’s Roadmap
- Vanguard: A Comprehensive Exploration Of The Map
- Navigating The African Continent: Understanding Longitude And Latitude
- Unpacking The Geography Of East Europe And Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
- Interstate 5: A Vital Artery Connecting The West Coast
- Navigating Paradise: A Comprehensive Guide To Sandals Resort Locations
- A Coastal Tapestry: Exploring Washington State’s Diverse Shoreline
- Navigating The Beauty Of Utah: A Comprehensive Guide To Printable Maps

Leave a Reply