A Journey To The Roof Of The World: Understanding Tibet’s Geographic Location
A Journey to the Roof of the World: Understanding Tibet’s Geographic Location
Related Articles: A Journey to the Roof of the World: Understanding Tibet’s Geographic Location
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Journey to the Roof of the World: Understanding Tibet’s Geographic Location. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey to the Roof of the World: Understanding Tibet’s Geographic Location
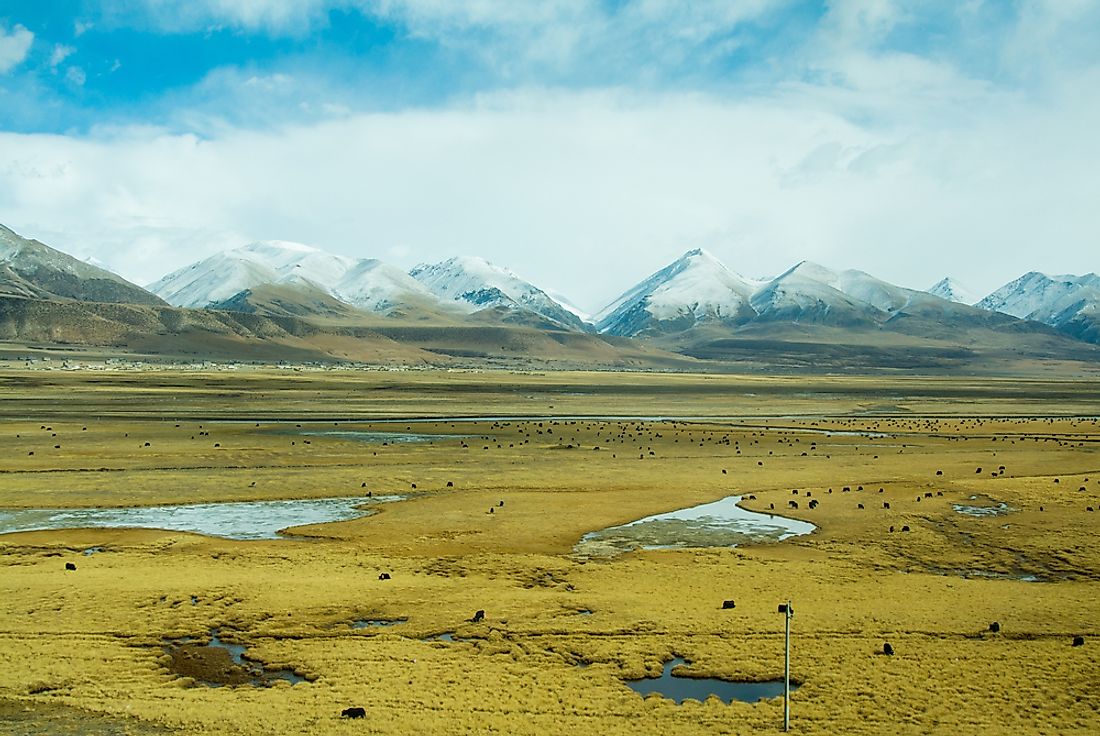

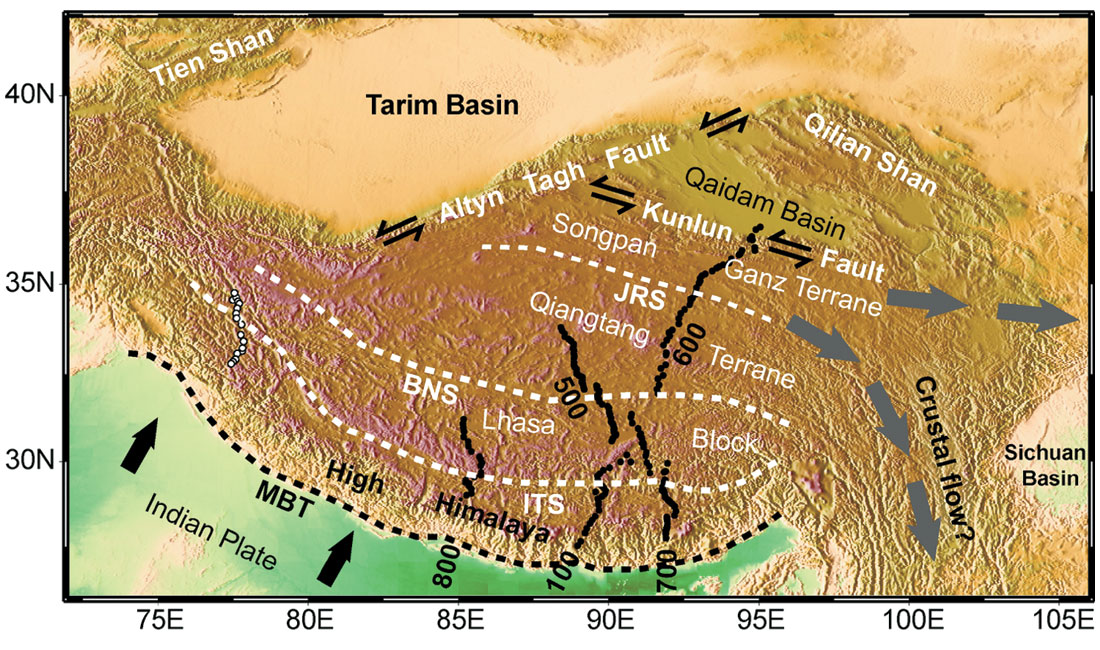
Tibet, often referred to as the "Roof of the World," holds a captivating allure for its unique landscape, rich culture, and historical significance. Situated in the heart of Asia, Tibet’s geographical position plays a pivotal role in shaping its environment, culture, and global importance.
A Plateau of Extremes: The Physical Geography of Tibet
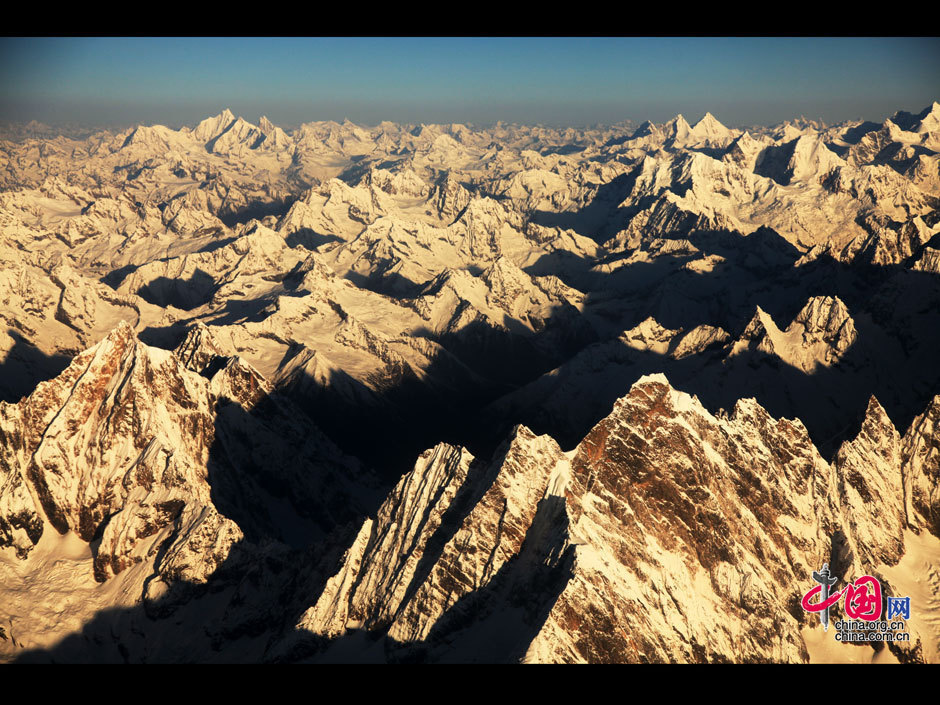
Tibet is characterized by its vast, high-altitude plateau, known as the Tibetan Plateau. This plateau, stretching across an area of over 2.5 million square kilometers, is the highest and largest plateau on Earth. Its average elevation is around 4,500 meters (14,764 feet), with some peaks reaching heights exceeding 8,000 meters (26,247 feet).
Where is Tibet on the Map?
Tibet is located in the southwestern part of China, occupying a significant portion of the country’s western border. It shares borders with several countries, including India, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar, and Pakistan. The region’s geographical location is a complex one, often subject to political and territorial disputes.
Key Geographic Features:
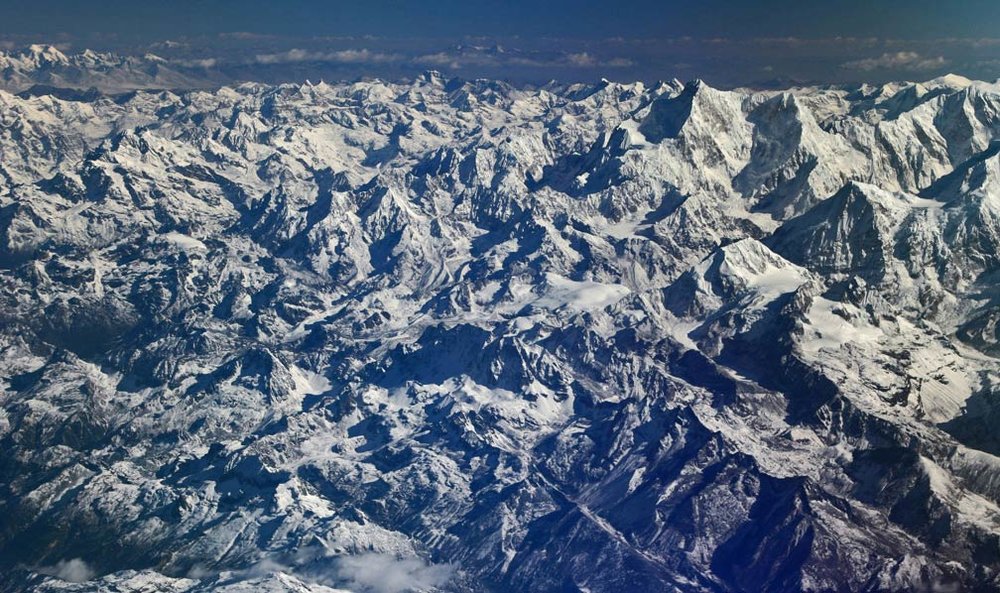
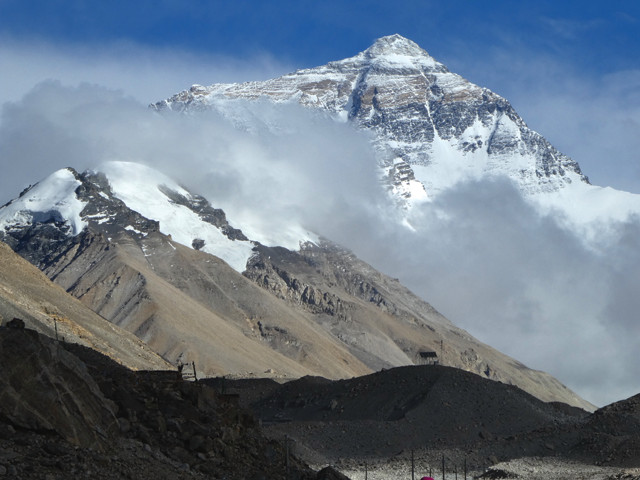
- The Himalayas: The mighty Himalayan mountain range, home to the world’s highest peaks, including Mount Everest, forms the southern border of Tibet. This formidable range serves as a natural barrier, influencing Tibet’s climate and isolating it from the Indian subcontinent.
- The Karakoram Range: To the west, the Karakoram range, another towering mountain chain, separates Tibet from Pakistan and parts of India. It is home to several prominent peaks, including K2, the world’s second-highest mountain.
- The Kunlun Mountains: In the north, the Kunlun Mountains run parallel to the Himalayas, forming a natural boundary between Tibet and the Tarim Basin, a vast desert region in northwest China.
- The Tibetan Plateau: The plateau itself is a vast, arid, and sparsely populated region. Its high altitude and thin atmosphere create harsh conditions, with extreme temperature variations and limited rainfall.
The Importance of Tibet’s Location
Tibet’s geographical location has profound implications for its environment, culture, and geopolitical significance:
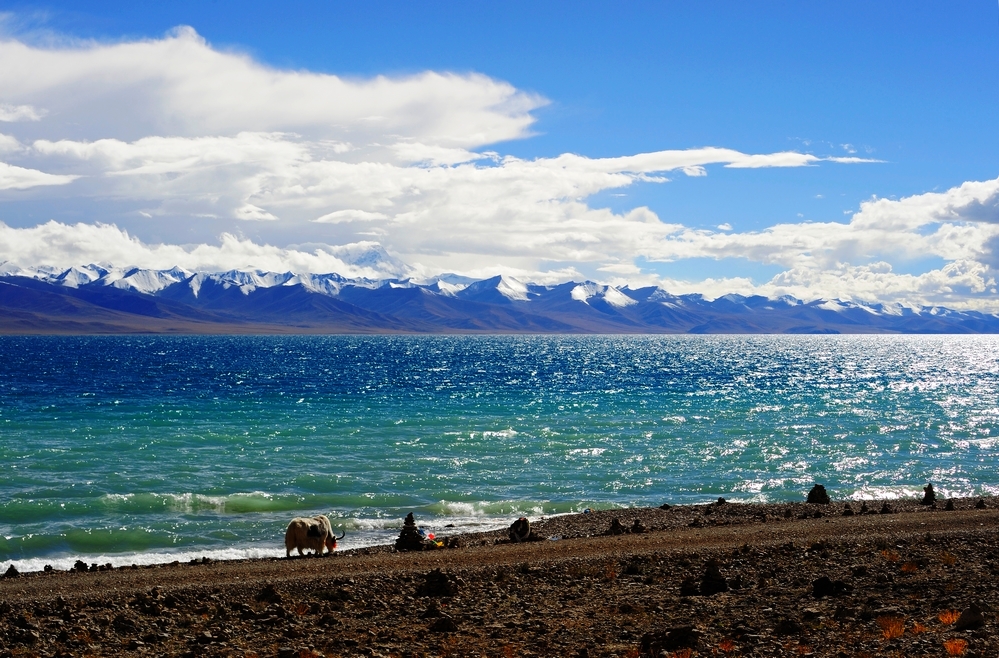
- Water Tower of Asia: Tibet is often referred to as the "Water Tower of Asia" due to its role in supplying water resources to major rivers, including the Yangtze, Yellow, Mekong, Indus, and Brahmaputra. These rivers, originating in the Tibetan Plateau, sustain millions of people across Asia.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: Despite its harsh environment, Tibet is a biodiversity hotspot, home to unique flora and fauna adapted to high altitudes. It is a refuge for endangered species like the snow leopard, Tibetan antelope, and red panda.
- Cultural Crossroads: Tibet’s location at the crossroads of different civilizations has fostered a rich and distinct culture. Its unique Buddhist traditions, art, and language have influenced neighboring regions, contributing to the cultural tapestry of Asia.
- Strategic Importance: Tibet’s strategic location, bordering several countries, has made it a subject of geopolitical interest throughout history. Its proximity to major trade routes and its potential for resource extraction have made it a vital region in regional power dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions about Tibet’s Location:
- What is the administrative status of Tibet? Tibet is an autonomous region of China, officially known as the Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR). However, its political status remains a subject of debate and contention, with some groups advocating for Tibetan independence.
- What is the climate like in Tibet? Tibet’s climate is characterized by its high altitude, resulting in cold winters and short, cool summers. The region receives limited rainfall, and its climate is generally arid.
- What are the major cities in Tibet? Lhasa, the capital of Tibet, is the largest and most important city. Other major cities include Xigaze, Shigatse, and Chamdo.
- What are the main economic activities in Tibet? Agriculture, tourism, and mineral extraction are the main economic activities in Tibet. The region is also rich in natural resources, including gold, copper, and hydropower.
Tips for Visiting Tibet:
- Obtain a Tibet Travel Permit: Due to its sensitive political situation, visitors require a special permit to enter Tibet. This permit can be obtained through authorized travel agencies.
- Acclimatize Gradually: Tibet’s high altitude can cause altitude sickness, so it’s essential to acclimatize gradually by spending a few days at lower altitudes before venturing into higher areas.
- Respect Local Customs: Tibet has a unique culture and traditions. Be respectful of local customs, dress modestly, and avoid taking photos of people without their permission.
- Plan Ahead: Tibet’s infrastructure is developing, but it can be challenging to travel within the region. Plan your itinerary carefully and book accommodations in advance.
Conclusion:
Tibet’s location on the "Roof of the World" is a testament to its unique geographical and cultural identity. Its high-altitude plateau, strategically positioned amidst towering mountain ranges and bordering several countries, has shaped its environment, culture, and global significance. Understanding Tibet’s geographical location is crucial for appreciating its role as a water tower, biodiversity hotspot, and cultural crossroads, as well as its geopolitical importance in the larger Asian context. While navigating the complexities of its political landscape, Tibet’s location continues to hold a captivating allure for travelers, researchers, and those interested in exploring the wonders of this extraordinary region.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey to the Roof of the World: Understanding Tibet’s Geographic Location. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Future: A Deep Dive Into SAP’s Roadmap
- Vanguard: A Comprehensive Exploration Of The Map
- Navigating The African Continent: Understanding Longitude And Latitude
- Unpacking The Geography Of East Europe And Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
- Interstate 5: A Vital Artery Connecting The West Coast
- Navigating Paradise: A Comprehensive Guide To Sandals Resort Locations
- A Coastal Tapestry: Exploring Washington State’s Diverse Shoreline
- Navigating The Beauty Of Utah: A Comprehensive Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply